TL;DR – A Master Service Agreement (MSA) is a legal contract that defines the terms and conditions for future transactions between two or more parties. It eliminates the need to renegotiate terms for each new project, standardizes services, reduces legal risks, and accelerates business operations.
In today’s complex business landscape, establishing clear, comprehensive frameworks for ongoing business relationships is essential for success. Master Service Agreements (MSAs) serve as the cornerstone of these relationships, creating a foundation of trust and clarity that supports efficient operations. This guide explores everything you need to know about MSAs: what they are, why they matter, and how they can transform your approach to business partnerships.
“Master Service Agreements aren’t just legal documents—they’re strategic assets that transform business relationships from transactional exchanges into collaborative partnerships built on clarity, trust, and mutual success.” – Jerry Levine, Chief Evangelist and GC, ContractPodAi
Understanding Master Service Agreements: The Foundation of Successful Business Relationships
A Master Service Agreement (MSA) is a comprehensive legal contract that establishes the fundamental terms and conditions governing an ongoing business relationship between two or more parties. Unlike single-project contracts, an MSA creates a framework that applies to multiple future transactions, projects, or services, eliminating the need to renegotiate basic terms for each new engagement.
The MSA is the constitutional document of your business relationship—it establishes the governing principles that all future activities will follow. As legal experts point out, MSAs are intended to outline the rights and responsibilities of the parties involved in an ongoing relationship rather than applying to one-time transactions. According to Wikipedia, a well-crafted MSA allows counterparties to use “sophisticated strategies to identify potential risks and create a strategy to mitigate them” without needing to create new agreements for every action between parties.
When Should You Use a Master Service Agreement?
MSAs are particularly valuable when:
- You anticipate multiple projects with the same vendor or client over an extended period
- You need recurring services from the same provider
- You want to standardize terms across multiple divisions or departments
- You seek to reduce the time and costs associated with contract negotiations
- You aim to establish consistent risk management protocols
The Anatomy of an Effective Master Service Agreement
A well-crafted MSA includes several critical components that protect all parties and create a clear operational framework. Here’s what makes up the backbone of an effective MSA:
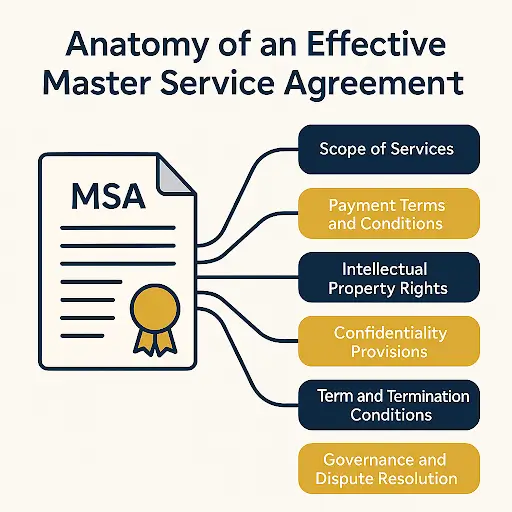
1. Scope of Services
This section defines what services the provider will deliver under the agreement. While the MSA won’t detail specific projects (those typically appear in subsequent Statements of Work), it establishes the categories of services covered and general parameters for how work will be performed.
A comprehensive scope of services helps prevent “scope creep”—the gradual expansion of work beyond what was initially agreed upon—by creating clear boundaries for what is and isn’t included in the relationship. Legal experts emphasize that clearly defining the scope of services acts as a roadmap for the vendor’s responsibilities, covering everything from software development to IT support to marketing services, depending on the business relationship.
2. Payment Terms and Conditions
The financial aspects of your business relationship deserve careful attention. A robust MSA should clearly outline:
- Rate structures and pricing models
- Payment schedules and cycles
- Invoicing procedures
- Late payment penalties
- Currency considerations for international agreements
- Tax responsibilities
For enterprise clients, the MSA often includes monthly billing cycles that streamline processes and reduce administrative burdens, as well as extended payment terms that improve cash flow management. Business experts note that enterprise procurement teams place high value on these operational benefits, with monthly billing becoming standard practice to replace weekly cycles and reduce administrative burden.
3. Intellectual Property Rights
In today’s knowledge economy, intellectual property (IP) provisions are more critical than ever. Your MSA should explicitly state:
4. Confidentiality Provisions
- Who owns the work products created
- How pre-existing IP can be used
- Licensing arrangements for any shared IP
- Restrictions on usage of proprietary information
- Protection mechanisms for trade secrets
Information security is paramount in business relationships. Your MSA should include robust confidentiality clauses that:
- Define what constitutes confidential information
- Specify how confidential information must be handled
- Outline the duration of confidentiality obligations
- Address exceptions to confidentiality requirements
- Establish remedies for confidentiality breaches
5. Term and Termination Conditions
Even the best business relationships may eventually end. Your MSA should provide clarity around:
- The initial term of the agreement
- Renewal procedures and terms
- Conditions for termination with cause
- Conditions for termination without cause
- Notice periods for termination
- Transition assistance requirements
- Post-termination obligations
6. Indemnification and Limitation of Liability
Risk allocation is one of the most crucial functions of an MSA. These sections should address:
- Indemnification obligations of each party
- Exclusions from indemnification
- Caps on liability
- Types of damages that are recoverable
- Insurance requirements
7. Governance and Dispute Resolution
Establishing clear governance mechanisms prevents minor disagreements from escalating into major disputes. Your MSA should include:
- Points of contact for different types of issues
- Escalation procedures for unresolved matters
- Required status meetings and reporting
- Dispute resolution mechanisms (mediation, arbitration, litigation)
- Governing law and venue provisions
The Strategic Value of Master Service Agreements: Beyond Legal Protection
While MSAs certainly provide crucial legal protection, their value extends far beyond risk management. A thoughtfully crafted MSA delivers strategic advantages that can transform your business operations.
Accelerating Business Velocity
MSAs drastically reduce the complexity of the negotiation process and speed it up for future projects and contracts. According to Thomson Reuters, this streamlined process “saves time and money for everyone involved.” By eliminating the need to negotiate standard terms repeatedly, organizations can:
- Launch new projects more quickly
- Respond faster to market opportunities
- Reduce administrative overhead
- Focus resources on delivery rather than paperwork
Enhancing Relationship Quality
Clear expectations foster stronger business relationships. An MSA sets the tone for collaboration by:
- Establishing transparent communication channels
- Defining performance standards
- Creating accountability mechanisms
- Building mutual understanding of priorities and constraints
Contract management experts explain that a well-drafted MSA spells out all terms and conditions upfront, reducing misunderstandings and conflicts during the course of the business relationship. This clarity can significantly reduce the potential for disputes and strengthen the foundation for long-term partnership.
Improving Financial Predictability
MSAs create financial stability through:
- Standardized pricing structures
- Clear payment schedules
- Defined budget approval processes
- Consistent resource allocation
Strengthening Compliance and Governance
In today’s complex regulatory environment, MSAs help organizations:
- Maintain consistent compliance standards across all engagements
- Implement uniform security protocols
- Establish clear audit trails
- Enforce corporate governance policies
Overcoming Common Challenges with Master Service Agreements

Despite their many benefits, MSAs can present challenges that must be carefully navigated. Being aware of these potential pitfalls allows you to create more effective agreements.
Challenge 1: Balancing Standardization and Flexibility
Legal specialists note that poorly drafted or overly rigid MSAs can lead to disputes, operational disruptions, and reputational damage. It’s crucial to balance the benefits of standardization with the need for flexibility to adapt to changing circumstances.
Solution: Design your MSA with modularity in mind. Create a strong core agreement with clearly defined mechanisms for adding project-specific terms through statements of work or order forms. Include provisions for periodic reviews and updates to the master agreement itself. Contract management professionals emphasize that the Master Service Agreement is negotiated once and remains in effect for a longer period of time while Statements of Work can be prepared and executed quickly with respect to the specific services needs of the customer, allowing for significant time and expense savings.
Challenge 2: Managing Scope Definition
Contract specialists warn that ambiguity in contracts can lead to assumptions that don’t match reality, creating disputes about obligations regarding the scope of services.
Solution: While maintaining flexibility, be precise about what services are covered under the MSA. Define key terminology clearly, and establish explicit processes for scope changes. Consider including examples or categories of in-scope and out-of-scope activities. Software development professionals recommend including the specific services that will be provided by the vendor as the starting point for drafting a comprehensive agreement, suggesting this section should function as a roadmap for the vendor’s responsibilities.
Challenge 3: Navigating Regulatory Compliance
MSAs must account for evolving regulatory requirements, particularly in highly regulated industries.
Solution: Include compliance sections that reference adherence to applicable laws rather than naming specific regulations that may change. Establish processes for updating compliance requirements as regulations evolve, and define responsibility for monitoring regulatory changes.
Challenge 4: Addressing Technological Evolution
Technology changes rapidly, making it challenging to create technology-related terms that remain relevant over a multi-year agreement.
Solution: Focus on outcomes and performance standards rather than specific technologies. Include technology refresh provisions and establish governance mechanisms for evaluating and implementing new technologies within the relationship.
Challenge 5: Managing Complex Relationships
Modern business relationships often involve multiple entities, divisions, or geographies, adding complexity to MSA implementation.
Solution: Use master agreement structures with subsidiary agreements for different business units or regions. Create clear hierarchies of documents and establish governance bodies with representatives from all key stakeholder groups.
Master Service Agreements Across Industries: Tailoring Your Approach
While the core principles of MSAs remain consistent, effective agreements recognize and address industry-specific considerations.

Technology and Software Development
Technology MSAs typically emphasize:
- Software licensing provisions
- Data security and privacy requirements
- Service level agreements with specific performance metrics
- Technology evolution and upgrade paths
- Source code escrow arrangements
Professional Services
In consulting and professional services, MSAs often focus on:
- Staff qualifications and certifications
- Knowledge transfer requirements
- Work product ownership and licensing
- Non-solicitation provisions
- Rate card structures and adjustments
Manufacturing and Supply Chain
Manufacturing-focused MSAs typically address:
- Quality assurance standards and testing
- Materials sourcing requirements
- Inventory management obligations
- Forecasting processes
- Warranty provisions
- Delivery schedules and logistics
Healthcare and Life Sciences
Healthcare MSAs must navigate:
- Patient data protection and HIPAA compliance
- Credentialing requirements
- Quality measurement frameworks
- Regulatory reporting obligations
- Research protocols and ethics
Real-World Applications: MSAs in Action
To understand how MSAs function in practice, consider these real-world applications:
Case Study 1: IT Services Management
A growing financial services firm establishes an MSA with a managed IT services provider. The MSA creates the framework for all IT support, with separate statements of work for helpdesk services, cybersecurity monitoring, cloud infrastructure management, and application development.
The MSA defines service level agreements, security requirements, and escalation procedures, while individual SOWs detail specific deliverables and timelines. When the firm decides to migrate to a new cloud platform, they simply create a new SOW rather than negotiating an entirely new agreement.
IT services professionals explain that service level agreements (SLAs) establish specific KPIs for delivered services, including system availability metrics for managed cloud infrastructure, network security, database management, and disaster recovery services. These metrics provide clear benchmarks for performance, making it easier to evaluate service quality and address any issues that arise.
Case Study 2: Marketing Agency Partnerships
A consumer products company establishes an MSA with its creative agency. The agreement outlines agency rates, intellectual property ownership, and approval processes.
For each marketing campaign, the parties create a project-specific statement of work defining deliverables, timelines, and budgets. This structure allows the company to maintain consistent terms while adjusting creative direction and campaign specifics for each product launch.
Case Study 3: Manufacturing Supply Chain
An automotive manufacturer creates MSAs with key component suppliers. The agreements establish quality standards, pricing frameworks, and logistics requirements.
Each component has a specific purchase order under the MSA umbrella, allowing for adjustments to quantities and delivery schedules without renegotiating fundamental terms. This arrangement provides stability while maintaining the flexibility needed to respond to market demands.
According to engineering experts, MSAs in manufacturing and engineering contexts allow teams to concentrate on pricing and efficiency because legal risks and protections of the parties have already been established in the MSA by the risk management and legal consultants. This enables operational teams to focus on delivery rather than constantly revisiting contract details.
Best Practices for Implementing Master Service Agreements
Implementing effective MSAs requires thoughtful preparation and ongoing management. Follow these best practices to maximize the value of your agreements:

1. Conduct Thorough Preliminary Analysis
Before drafting an MSA, analyze your business needs and objectives:
- Identify all stakeholders and gather their requirements
- Review past agreements to identify pain points and opportunities
- Assess industry standards and competitive practices
- Evaluate regulatory requirements and compliance considerations
Legal technology experts highlight the importance of this initial analysis, noting that a well-structured master service agreement review process is essential to streamline your legal work.
2. Develop a Balanced Negotiation Strategy
Approach MSA negotiations strategically:
- Distinguish between “must-have” and “nice-to-have” provisions
- Prepare fallback positions for key terms
- Document negotiation rationales for future reference
- Consider relationship impacts alongside legal protections
3. Create Clear Implementation Processes
Develop systems to operationalize your MSA:
- Create templates for statements of work and order forms
- Establish approval workflows for new projects
- Develop training programs for staff using the MSA
- Build monitoring tools for compliance and performance
Business advisors emphasize that over the course of the Master Service Agreement, naturally, the parties will become increasingly familiar with the precise terms of the contract. This familiarity creates an ease of reference in dealing with any issues, leading to fewer disputes and any disputes being resolved more efficiently where they do arise. Proper implementation processes amplify this benefit.
4. Establish Effective Governance Mechanisms
Create structures to manage the relationship over time:
- Define escalation paths for operational issues
- Schedule regular relationship review meetings
- Establish change management processes
- Create performance dashboards and reporting systems
5. Plan for Evolution and Updates
Recognize that business needs change over time:
- Schedule periodic MSA reviews
- Document lessons learned from implementation
- Create amendment processes that maintain agreement integrity
- Build flexibility into the agreement structure
In Summary: Transforming Business Relationships with Strategic MSAs
Master Service Agreements are more than legal documents—they’re strategic tools that can transform how organizations manage their most important business relationships. By establishing clear expectations, streamlining operations, and providing a framework for growth, well-crafted MSAs create the foundation for successful long-term partnerships.
As business environments become increasingly complex, the value of strong foundational agreements only grows. Organizations that master the art of creating effective MSAs gain a significant competitive advantage through enhanced operational efficiency, reduced risk, and stronger business relationships.
Business and legal experts agree that MSAs create solid foundations for long-term business relationships. Their structured framework aligns perfectly with enterprise procurement and approval processes while remaining flexible enough for growth. The most successful organizations recognize this dual value, viewing MSAs not merely as legal necessities but as strategic assets that drive business success.
For legal teams, MSAs represent an opportunity to move beyond traditional transactional roles and become strategic partners in business success. By crafting agreements that balance protection with enablement, legal professionals can help their organizations build the collaborative frameworks needed to thrive in today’s dynamic business landscape.
Harvard University’s Office for Sponsored Programs highlights the importance of proper agreement management, providing structured approaches for identifying and routing legal agreements. This institutional perspective underscores how critical these frameworks are for organizations of all types, from academic institutions to corporations.
At ContractPodAi, we’re committed to helping organizations transform their approach to contract management through innovative technology and best practices. Our AI-powered contract management platform streamlines the creation, negotiation, and management of MSAs and other complex agreements, turning contract management from an administrative burden into a strategic advantage.
Ready to transform your approach to Master Service Agreements? Contact our team today to learn how ContractPodAi can help you create more effective agreements and unlock the full strategic value of your business relationships.


