Published: March 20, 2025
Updated: July 3, 2025

The call came at 6:47 AM. Sarah Chen, Chief Procurement Officer at a mid-sized electronics manufacturer, learned that overnight tariff announcements would increase her company’s import costs by $3.2 million annually. Within hours, three suppliers demanded contract renegotiations, threatening supply disruptions if their requests were denied.
Sarah’s story reflects a common challenge. Current tariff policies have increased the US average effective tariff rate to 21.9%, the highest since 1909, creating an environment where procurement professionals face unprecedented challenges. However, companies that have built tariff protection into their contracts navigate these disruptions more effectively.
This guide provides seven essential strategies for building tariff-resilient contracts, based on proven approaches that help procurement professionals maintain stable operations regardless of trade policy changes.
Strategy 1: Calculate Your True Tariff Exposure
Most procurement teams underestimate their tariff exposure because they focus only on direct costs. Tariff impacts extend beyond the obvious rate increases to include secondary costs that can significantly amplify the total impact.

Understanding the Full Cost Impact
Motor vehicle prices have risen 15.6% in the short-run due to current tariffs, equivalent to an additional $5,700 to the average 2024 new car. This demonstrates how tariffs cascade through supply chains, affecting not just direct purchases but all downstream costs.
To calculate comprehensive tariff exposure, consider these cost categories:
- Direct Tariff Impact: Base import value × applicable tariff rate
- Secondary Cost Impact: Increased logistics costs, expedited shipping, alternative sourcing premiums
- Operational Disruption Costs: Production delays, inventory adjustments, supplier switching costs
- Relationship Management Costs: Legal fees, renegotiation time, contract updates
Building Response Capability
Companies that can respond quickly to tariff announcements minimize disruption costs. This requires contract language that enables rapid adaptation, which we’ll cover in the following strategies.
Strategy 2: Clarify Payment Responsibility
Unclear payment responsibility language leads to costly disputes when tariff changes occur. The solution involves creating clear frameworks that eliminate ambiguity before contracts are signed.
Enhanced Incoterms Framework
Standard Incoterms need additional clarification to address tariff volatility:
Enhanced FOB (Free on Board):

- Standard definition: Buyer assumes responsibility once goods are loaded
- Tariff clarification: “Buyer responsible for all tariffs implemented after contract signing date, with supplier providing 48-hour notification of any rate changes affecting pending shipments”
Strategic CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight):
- Standard definition: Seller covers transportation costs
- Tariff clarification: “Seller responsible for transportation costs based on rates at contract signing. Tariff increases above 3% trigger automatic price review clause within 30 days”
Comprehensive DDP (Delivered Duty Paid):
- Standard definition: Seller assumes all costs including tariffs
- Tariff clarification: “Seller absorbs tariff increases up to 5% of contract value. Increases exceeding this threshold trigger shared cost mechanism”
Preventing Payment Disputes
Clear contract language prevents misunderstandings by specifying:
- Tariff Monitoring Assignment: Which party monitors trade policy changes
- Notification Requirements: Timeline and documentation for tariff change communications
- Cost Allocation Methods: Formulas for sharing unexpected costs
Strategy 3: Avoid Critical Contract Mistakes
Several common contract mistakes transform manageable tariff adjustments into business-threatening crises. Understanding these pitfalls and their solutions can protect your organization from significant costs.
Mistake #1: Fixed-Price Contracts Without Flexibility
The Problem: Nine in ten supply chain leaders encountered disruptions in 2024, yet many contracts still lack flexibility mechanisms. Fixed-price contracts without adjustment clauses create situations where suppliers face margin compression and buyers risk supply disruptions.

The Impact: When apparel prices faced 31% tariff increases, companies with inflexible contracts experienced supplier disputes and quality issues as suppliers struggled to maintain profitability.
The Solution: Include graduated flexibility mechanisms that provide adjustment options at multiple threshold levels, preventing catastrophic failures while maintaining cost predictability.
Mistake #2: Outdated Force Majeure Language
The Problem: Traditional force majeure clauses focus on natural disasters and fail to address government policy changes. Shipping costs from China to the US East Coast increased 193% between October 2023 and February 2024, yet most force majeure clauses wouldn’t cover such policy-driven changes.
The Solution: Update force majeure language to specifically address:
- Government trade policy changes exceeding defined thresholds
- Infrastructure disruptions affecting trade routes
- Currency fluctuations beyond normal business ranges
- Export/import license modifications impacting contracted goods
Mistake #3: Poor Supply Chain Visibility
The Problem: The share of companies with good visibility into deeper supply chain levels fell by seven percentage points in 2024. With average lead times for production materials at 79 days, poor visibility leaves insufficient time for effective mitigation.
The Solution: Require suppliers to provide detailed sub-supplier information and country-of-origin documentation, creating early warning systems for potential tariff exposure.
Strategy 4: Essential Contract Clauses for Tariff Protection
Effective tariff protection requires specific contract language that addresses the unique challenges of trade policy volatility. These proven clause templates provide the foundation for tariff-resilient contracts.
Dynamic Price Adjustment Mechanism
Traditional price adjustment clauses often lack the specificity needed for tariff situations. Here’s proven language that balances supplier protection with buyer cost control:
“TARIFF COST ADJUSTMENT PROTOCOL: If government-imposed tariffs on contracted goods increase by more than 2% during the contract term, Supplier may adjust pricing to reflect documented additional costs, subject to the following conditions:
(a) 15-day advance written notice with official tariff documentation
(b) Cost increase capped at actual tariff amount plus reasonable administrative costs (not to exceed 5% of tariff increase)
(c) Buyer retains right to third-party verification of claimed costs
(d) Price adjustments become effective 30 days after proper notification
(e) Total contract price increases limited to 15% without triggering renegotiation rights”
Key Benefits: The 2% threshold filters out minor fluctuations, while the 15% cap prevents excessive cost increases.
Modern Force Majeure Framework
Enhanced force majeure provisions address 21st-century trade realities:
“EXPANDED FORCE MAJEURE EVENTS include government actions affecting international trade, specifically:
- Implementation of new tariffs exceeding 5% on contracted goods
- Changes in trade agreement status affecting duty rates
- Export/import restrictions preventing normal business operations
- Transportation route closures lasting more than 14 days
- Currency fluctuations exceeding 10% against baseline exchange rates
Upon Force Majeure declaration, parties shall immediately enter 30-day mitigation period with shared cost responsibility and alternative sourcing exploration.”
Automatic Renegotiation Triggers
Rather than waiting for problems to escalate, include automatic review triggers:
- Tariff changes exceeding 10% trigger mandatory contract review within 45 days
- New trade restrictions affecting contracted goods activate alternative sourcing discussions
- Supplier country trade status changes initiate risk assessment protocols
- Currency fluctuations beyond 15% activate pricing review mechanisms
Accelerated Dispute Resolution
Traditional dispute resolution is too slow for tariff-related issues. Use this three-tier approach:
- Immediate Response (Days 1-14): Direct executive consultation with documented solution attempts
- Mediation Phase (Days 15-45): Third-party mediation with industry expertise in trade policy
- Arbitration Phase (Days 46-60): Expedited arbitration with trade-specialized arbitrators
Strategy 5: Leverage Technology for Proactive Tariff Management
Moving from reactive to predictive tariff management requires strategic technology integration that goes beyond basic contract storage.
Automated Risk Detection
Advanced contract management platforms like ContractPodAi’s Leah Intelligence can analyze contract portfolios to identify tariff vulnerabilities that manual reviews might miss.
Key Capabilities:
- Real-time scanning of trade policy databases
- Automated flagging of contracts lacking tariff protection
- Risk scoring based on supplier location and product categories
- Predictive modeling for potential tariff exposure
Obligation Monitoring Systems
Automated systems can monitor contract obligations and alert teams to upcoming deadlines or trigger events.
Essential Features:
- Automated alerts for tariff rate changes affecting specific contracts
- Deadline tracking for renegotiation windows
- Documentation requirements for cost pass-through claims
- Supplier performance monitoring against tariff-related obligations
Predictive Analytics Benefits
Companies using advanced analytics gain additional preparation time before tariff changes impact operations. This early warning capability is crucial given that disruptions can take an average of two weeks to plan and execute a response.
Applications Include:
- Pattern recognition in trade policy announcements
- Supplier risk assessment based on geographic and political factors
- Cost impact modeling for various tariff scenarios
- Supplier mix recommendations for risk diversification
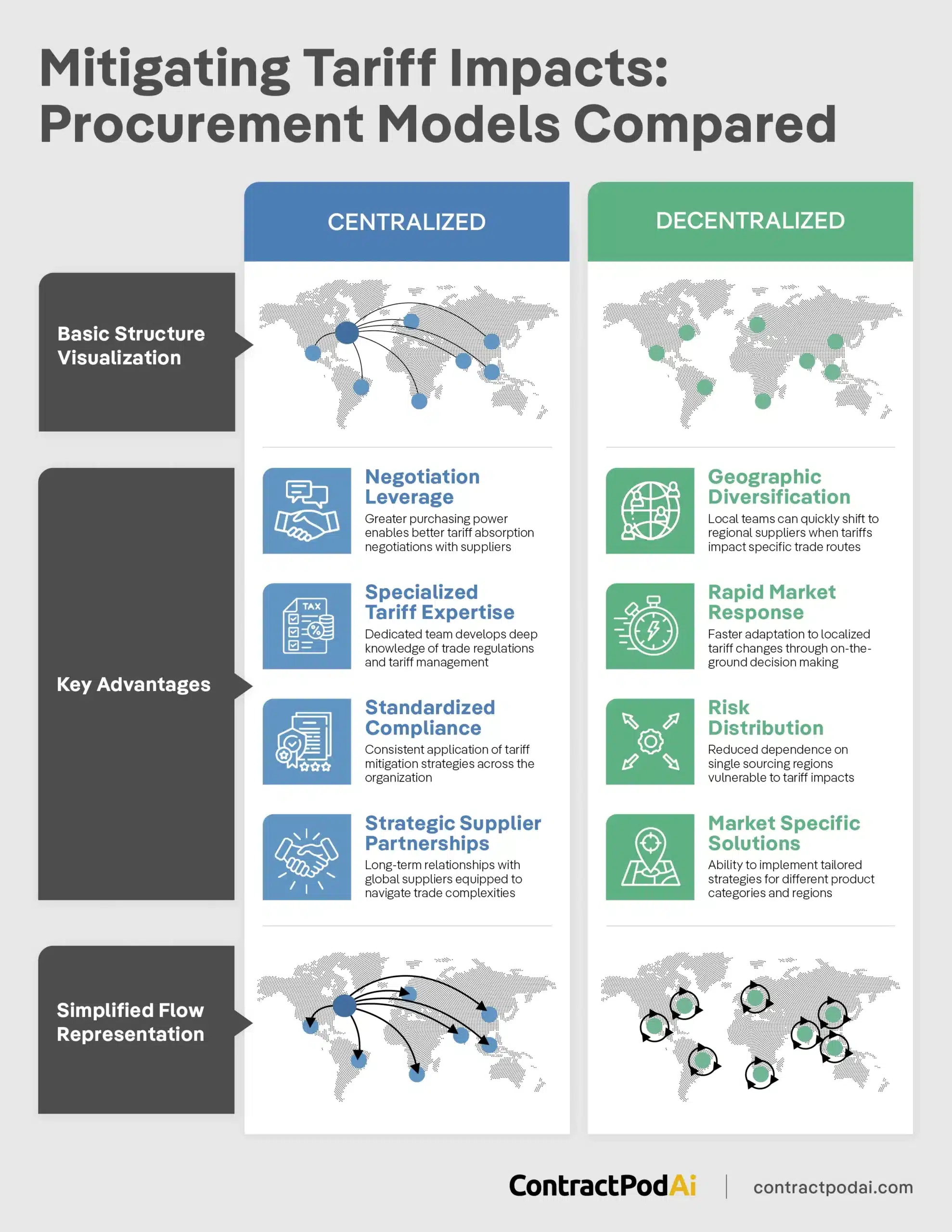
Strategy 6: Build Collaborative Supplier Relationships
Companies that thrive during tariff volatility strengthen supplier relationships through collaborative risk management rather than simply transferring risks or switching suppliers.
Strategic Supplier Assessment

While 97% of companies surveyed are reconfiguring their supply chains, the most successful take a collaborative approach.
Four-Quadrant Assessment Framework:
High Value, High Risk: Key suppliers in tariff-exposed regions
- Strategy: Joint investment in alternative manufacturing capabilities
- Implementation: Shared cost agreements for establishing secondary production sites
High Value, Low Risk: Strategic suppliers in favorable trade environments
- Strategy: Expanded partnership and increased volume commitments
- Implementation: Long-term contracts with preferential terms
Low Value, High Risk: Transactional suppliers in exposed regions
- Strategy: Gradual transition to alternative sources
- Implementation: Phased reduction with clear timeline communication
Low Value, Low Risk: Standard suppliers in stable environments
- Strategy: Maintain current relationships with standard terms
- Implementation: Regular monitoring without major changes
Collaborative Risk Management
Effective supplier partnerships involve shared responsibility for managing tariff risks:
- Joint Planning: Work together on scenario planning and mitigation strategies
- Shared Investment: Co-invest in alternative sourcing or manufacturing capabilities when feasible
- Transparent Communication: Regular briefings on trade policy developments and potential impacts
- Flexible Agreements: Contract terms that allow for collaborative problem-solving during disruptions
Communication Framework
Proactive Engagement Strategies:
- Monthly supplier briefings on trade policy developments
- Quarterly risk assessment sessions with key suppliers
- Annual strategic planning workshops including tariff scenario planning
- Real-time communication protocols for policy changes
Strategy 7: Implementation Roadmap for Tariff Resilience
This implementation framework provides step-by-step guidance for building tariff-resilient procurement operations.

90-Day Implementation Timeline
Phase 1: Assessment and Foundation (Days 1-30)
Week 1: Portfolio Risk Analysis
- Calculate tariff exposure using comprehensive framework
- Identify top 20 suppliers by tariff risk and business impact
- Document current contract protection levels
Week 2: Contract Audit
- Review existing contracts for tariff-related language gaps
- Categorize contracts by protection level and renewal timeline
- Prioritize updates based on risk and upcoming renewals
Week 3: Technology Evaluation
- Assess current contract management capabilities
- Evaluate platforms for automated tariff monitoring
- Develop technology integration plan
Week 4: Stakeholder Alignment
- Brief executive leadership on tariff risk exposure
- Secure budget for contract updates and technology investment
- Establish procurement team training schedule
Phase 2: Implementation and Integration (Days 31-60)
- Supplier Engagement: Begin discussions with key suppliers about tariff scenarios and mitigation strategies
- Contract Updates: Start implementing new clause language for contracts up for renewal
- Technology Deployment: Begin platform implementation and team training
- Process Development: Establish new workflows for tariff monitoring and response
Phase 3: Optimization and Scaling (Days 61-90)
- Full Portfolio Application: Apply new standards to all relevant contracts
- Supplier Integration: Complete risk assessment discussions with all key suppliers
- Technology Optimization: Fine-tune automated systems and reporting
- Performance Measurement: Establish metrics for ongoing tariff risk management
Ongoing Management Protocol
Monthly Reviews:
- Trade policy monitoring and impact assessment
- Supplier performance against tariff obligations
- Contract portfolio health checks
Quarterly Assessments:
- Comprehensive risk exposure analysis
- Supplier relationship quality evaluation
- Technology platform performance review
- Process optimization opportunities
Annual Strategic Planning:
- Full contract portfolio overhaul
- Supplier diversification strategy updates
- Technology roadmap advancement
- Team capability development
Success Metrics
Track your organization’s tariff resilience using these key indicators:
Response Time Metrics:
- Average time from tariff announcement to impact assessment
- Days required to implement mitigation strategies
- Supplier communication response times
Financial Protection Metrics:
- Percentage of contracts with adequate tariff protection
- Actual tariff impact versus budgeted exposure
- Cost of tariff mitigation as percentage of total procurement spend
Relationship Quality Metrics:
- Supplier satisfaction with tariff handling processes
- Number of tariff-related contract disputes
- Supplier retention rates during tariff volatility
Building Your Tariff-Resilient Future
The procurement landscape has fundamentally changed. With current tariff policies expected to reduce US real GDP growth by 0.8 percentage points, effective tariff management has become a critical business capability. Organizations that implement these seven strategies don’t just survive trade policy volatility—they maintain competitive advantages through stable operations.
The most successful companies share common characteristics: they prepare proactively rather than react defensively, they view supplier relationships as partnerships rather than transactions, and they leverage technology to predict problems rather than just manage them.
Your contracts should enable business agility, not constrain it. The frameworks, templates, and strategies outlined in this guide provide the foundation for building procurement operations that thrive regardless of trade policy changes. With 93% of senior supply chain executives intending to make their supply chains more flexible and resilient, the question isn’t whether to invest in tariff resilience—it’s how quickly you can implement these proven strategies.
Companies that master strategic contract management for tariff risks gain significant competitive advantages: stable supply chains during trade disruptions, stronger supplier relationships through collaborative risk management, and predictable costs even in volatile trade environments.
Success requires treating tariff management as an ongoing strategic capability rather than a reactive emergency response. The key elements include proactive planning, clear contractual frameworks, collaborative supplier relationships, and technology-enabled intelligence. Trade policies will continue to evolve, but organizations with robust tariff-resilient contract management will navigate these challenges successfully while their competitors struggle with disputes, disruptions, and unexpected costs.
Ready to transform your procurement operations from tariff-vulnerable to tariff-resilient? Schedule a demo with ContractPodAi to discover how Leah Intelligence can automate tariff risk analysis, identify contract vulnerabilities, and help you implement the strategic frameworks outlined in this guide. Your supply chain’s stability depends on the decisions you make today.


