Last Updated: October 22, 2025
Quick Answer: Manufacturing contracts are legally binding agreements between businesses and manufacturers that define production specifications, quality standards, payment terms, and intellectual property rights. In 2025, these contracts have evolved from simple legal documents into strategic risk management tools that address supply chain volatility, ESG compliance, cybersecurity requirements, and AI-driven contract monitoring. McKinsey reports that 85% of supply chain professionals navigate more risks than ever, making robust manufacturing contracts essential for business resilience.
Key Takeaways [TL;DR]
- Manufacturing contracts in 2025 serve as strategic risk management tools, not just legal paperwork, addressing supply chain disruptions, tariff volatility, and ESG compliance requirements
- There are 17 distinct types of manufacturing contracts, including OEM, ODM, Private Label, White Label, and industry-specific agreements for pharmaceuticals, food, textiles, and automotive sectors
- Essential contract clauses include IP rights, quality control, payment terms, force majeure provisions, and compliance requirements—contracts without these protections have led to costly recalls and litigation
- The manufacturing AI market is projected to reach $155 billion by 2030, with 77% of manufacturers having implemented AI to some extent in 2024 to streamline operations and contract management
- AI-powered contract lifecycle management is transforming how agreements are created and monitored, with agentic AI systems now analyzing thousands of clauses, predicting supplier risks, and triggering compliance alerts in real-time
What Sets Manufacturing Contracts Apart in 2025?

If you’ve spent any time in manufacturing, you know contracts aren’t just “legal paperwork.” They’re the backbone of how partnerships actually work—who’s making what, who’s on the hook when something goes wrong, and how to keep things moving when disruption hits (and it always does).
Disruption has become business as usual. McKinsey reports that 85% of supply chain professionals are navigating more risks than ever. At the same time, the manufacturing AI market is projected to reach $155 billion by 2030, with three out of four organizations already adopting AI to streamline operations and contract management. That shift is already reshaping how contracts are written and managed.
Today’s agreements need to go well beyond assigning responsibilities. They have to anticipate volatility in raw materials and tariffs, address cybersecurity risks directly, and build in mechanisms for ESG and sustainability compliance. And because no team has the bandwidth to manage all that complexity manually, AI-powered contract lifecycle management has become essential—simplifying risk tracking, supplier compliance, and performance monitoring.
This guide walks you through 17 types of manufacturing contracts, the clauses that actually protect your organization, and the compliance and negotiation strategies that help manufacturers build resilience instead of just reacting to the next crisis.
What Is a Manufacturing Contract and Why Does It Matter?
A manufacturing contract is a legally binding agreement between your business and a manufacturer that defines how goods will be produced or what services will be provided. Think of it as the rulebook for your business relationship, covering product specs, quality standards, payment terms, intellectual property rights, and more.
Unlike service agreements or purchase orders, manufacturing contracts dig into production details—capacity, material sourcing, tooling, and even specialized processes. In 2025, they’ve become strategic risk management tools, not just legal formalities.
Understanding the different types of manufacturing relationships is also key when deciding what kind of contract to pursue:
- Contract Manufacturing vs. Toll Manufacturing – Contract manufacturing involves outsourcing production to a third-party manufacturer who handles the entire process, while toll manufacturing refers to hiring a manufacturer to process materials you provide using their equipment and facilities.
- OEM vs. ODM Relationships – Original Equipment Manufacturer (OEM) agreements involve producing goods to your specifications, while Original Design Manufacturing (ODM) agreements allow manufacturers to design and produce goods that you rebrand and sell.
- Private Label vs. White Label Manufacturing – Private label involves exclusive production for your brand, while white label refers to generic products that multiple companies can rebrand and sell.
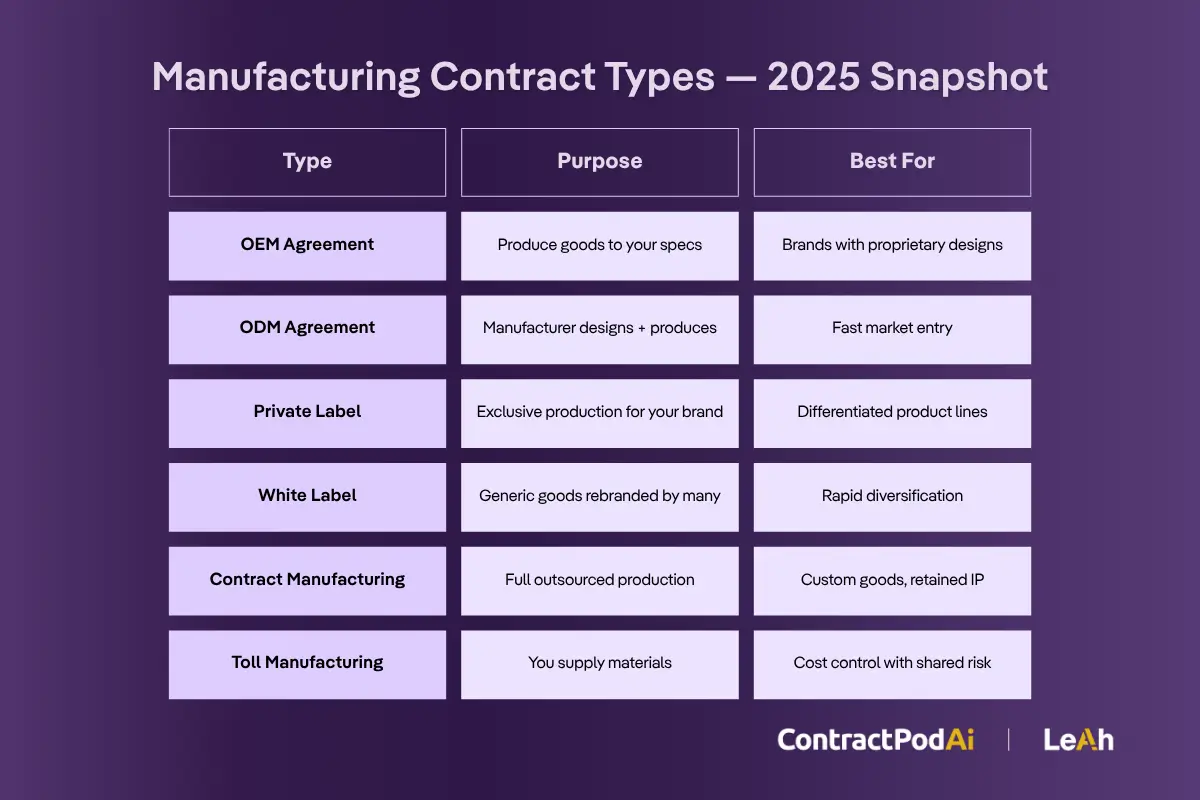
Which 17 Types of Manufacturing Contracts Are Most Relevant?
A thorough understanding of manufacturing contracts is essential for tailoring agreements to specific business needs. Here’s a breakdown of the most common and emerging types of contracts in 2025:
| Contract Type | Purpose | Key Clauses | Typical Use Case | Industry Examples | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Contract Manufacturing Agreement | Terms for producing goods to buyer specifications | Payment Terms, Quality Control, IP Rights | Businesses hiring manufacturers to produce custom goods | Electronics, pharmaceuticals, automotive components | Companies wanting to outsource production while maintaining design control |
| Manufacturing Service Agreement | Defines manufacturing-related services (e.g., consulting, R&D) | Service Scope, Confidentiality, Deliverables | Engaged for consulting or specialized equipment usage | Industrial consulting, process optimization | Businesses needing specialized manufacturing expertise |
| Subcontractor Manufacturing Agreement | Outlines responsibilities when work is outsourced to subcontractors | Subcontractor Obligations, Quality Control, Liability | When third parties handle specific production components | Construction, aerospace, complex manufacturing | Managing multi-tier supply chains with specialized components |
| Supply Chain Agreement | Comprehensive coverage for supply chain management | Risk Allocation, Delivery Terms, Compliance | Managing long-term supplier relationships and logistics | Automotive, consumer goods, retail | Companies with complex, multi-vendor supply chains |
| Original Equipment Manufacturer (OEM) Agreement | Manufacturer produces goods to company specifications | Intellectual Property, Licensing Terms, Quality Standards | Used when outsourcing production while retaining branding control | Technology hardware, automotive parts, medical devices | Brands with proprietary designs requiring specialized manufacturing |
| Original Design Manufacturing (ODM) Agreement | Manufacturer designs and produces goods for buyer rebranding | Ownership Rights, Product Development, Exclusivity | Companies wanting to brand products designed by manufacturer | Consumer electronics, fashion accessories, home goods | Businesses seeking quick market entry with proven designs |
| Turnkey Manufacturing Agreement | Manufacturer handles entire production process from design to delivery | Ownership, Timeline, Delivery Specifications, Project Management | Complete outsourcing of manufacturing aspects | Industrial equipment, custom machinery, specialized products | Companies wanting minimal manufacturing involvement |
| Electronic Contract Manufacturing Agreement | Manufacturer produces electronic components or devices | Quality Standards, Confidentiality, Testing Protocols | Technology and electronics industries | Smartphones, computers, IoT devices, semiconductors | Tech companies focusing on design and marketing |
| White Label Manufacturing Agreement | Produces generic goods sold under retailer’s brand | Rebranding Rights, Quality Standards, Volume Requirements | Retailers seeking quick branding solutions for generic products | Consumer goods, supplements, basic electronics | Retailers wanting fast product diversification |
| Private Label Manufacturing Agreement | Produces goods exclusively for specific brand | Exclusivity, Product Specifications, Territory Rights | Brands wanting unique products with exclusive access | Cosmetics, food products, apparel | Companies building distinctive product lines |
| Private Label Supply Agreement | Governs supply of goods for exclusive branding by buyer | Supply Terms, Exclusivity, Minimum Orders | Retailers wanting products manufactured under their private label | Grocery, retail chains, e-commerce platforms | Large retailers developing proprietary product lines |
| Distribution Agreement | Governs distribution of products to end customers | Territory, Pricing, Marketing Responsibilities | Manufacturers defining terms with distributors | Consumer goods, industrial equipment, software | Manufacturers expanding market reach through partners |
| Value-Added Reseller (VAR) Agreement | Allows resellers to add value before selling | Licensing, Modification Rights, Support Requirements | Software, electronics, and technology industries | IT solutions, specialized software, technical equipment | Technology companies leveraging partner expertise |
| Textile Manufacturing Agreement | Terms for producing textiles or apparel | Design Approvals, Production Volume, Compliance | Fashion and apparel industry | Clothing, fabrics, accessories, footwear | Fashion brands and apparel companies |
| Pharmaceutical Manufacturing Agreement | Produces drugs and medical products under strict regulations | Compliance, Safety Standards, Validation | Pharmaceutical companies ensuring regulatory adherence | Prescription drugs, medical devices, supplements | Healthcare companies requiring FDA compliance |
| Food Manufacturing Agreement | Covers production and packaging of food products | Food Safety, Labeling Requirements, Traceability | Food industry for safe and consistent production | Packaged foods, beverages, nutritional products | Food brands prioritizing safety and compliance |
| Component Manufacturing Agreement | Focuses on producing specific parts or components | Design Specifications, Warranty Terms, Integration | Companies assembling final products from outsourced components | Automotive parts, electronic components, machinery | Assembly-focused businesses requiring reliable component supply |
Emerging trend: ESG-focused agreements are rising fast—embedding sustainability and carbon accountability into traditional contracts. See ContractPodAi for CPG & Manufacturing for how AI is helping manufacturers adapt.
Which Clauses Should Manufacturing Contracts Include?
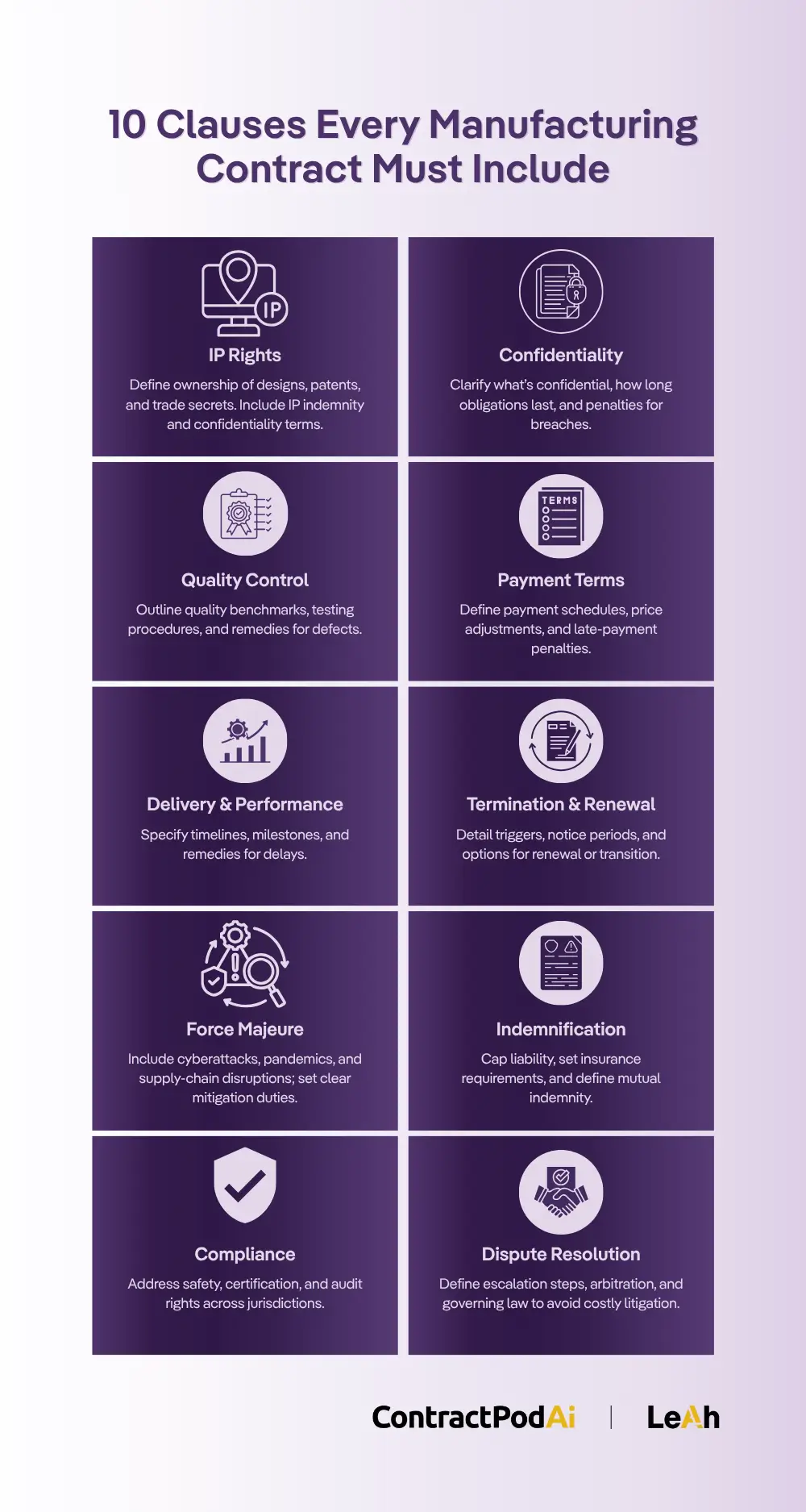
To build an effective manufacturing contract, the following clauses are essential for protecting your business interests and ensuring successful partnerships:
1. Intellectual Property Rights
Why Critical: Protects ownership of designs, patents, proprietary processes, and trade secrets. Without clear IP clauses, disputes over ownership can lead to costly litigation and loss of competitive advantages.
Key Elements: Define ownership of existing IP, new developments, licensing terms, and protection mechanisms. Include provisions for IP indemnification and confidentiality of proprietary information.
2. Confidentiality/Non-Disclosure
Why Critical: Safeguards sensitive business information, including manufacturing processes, customer data, pricing strategies, and technical specifications from unauthorized disclosure.
Key Elements: Specify scope of confidential information, duration of obligations (typically 3-5 years), permitted disclosures, and penalties for breaches.
3. Quality Control & Product Specifications
Why Critical: Ensures consistency in product quality and provides mechanisms for addressing defects. Vague quality standards are a leading cause of manufacturing disputes.
Key Elements: Detailed technical specifications, quality standards, testing procedures, acceptance criteria, and remedies for non-conforming products.
4. Payment Terms & Pricing
Why Critical: Establishes clear payment schedules and pricing mechanisms to avoid cash flow disputes and ensure fair compensation for both parties.
Key Elements: Payment schedules, price adjustment mechanisms, penalties for late payments, and provisions for material cost fluctuations.
5. Delivery & Performance Terms
Why Critical: Specifies delivery timelines, performance milestones, and remedies for delays. Clear delivery terms prevent disputes and ensure supply chain continuity.
Key Elements: Delivery schedules, milestone payments, performance penalties, and provisions for expedited delivery when needed.
6. Termination & Renewal Clauses
Why Critical: Defines how contracts can end or be extended, protecting both parties’ interests during transitions and providing flexibility for changing business needs.
Key Elements: Termination triggers, notice periods, transition procedures, and renewal options with updated terms.
7. Force Majeure & Risk Allocation
Why Critical: 2025 considerations include cyber attacks, supply chain disruptions, and pandemic-related shutdowns. These clauses protect parties from unforeseeable events.
Key Elements: Definition of force majeure events, notification procedures, mitigation obligations, and risk-sharing mechanisms for extended disruptions.
8. Indemnification & Liability
Why Critical: Limits financial exposure and defines responsibility for damages, defects, or third-party claims arising from manufacturing activities.
Key Elements: Liability caps, insurance requirements, mutual indemnification provisions, and exclusions for certain types of damages.
9. Compliance & Regulatory Requirements
Why Critical: Ensures adherence to industry-specific regulations, safety standards, and legal requirements that vary by jurisdiction and industry.
Key Elements: Regulatory compliance obligations, certification requirements, audit rights, and procedures for regulatory changes.
10. Dispute Resolution
Why Critical: Provides efficient mechanisms for resolving conflicts without resorting to costly litigation, maintaining business relationships where possible.
Key Elements: Escalation procedures, arbitration clauses, governing law provisions, and jurisdiction selection for legal proceedings.
The risks of missing these protections are real. Companies have faced significant losses due to inadequate IP clauses, with research showing that weak intellectual property protections can directly harm innovation and competitive advantage (University of Alberta). Vague quality specifications have contributed to costly product recalls, which in turn have fueled liability disputes and brand damage (JD Supra). And when the COVID-19 pandemic struck, many businesses found themselves unprotected because their contracts lacked explicit force majeure language, leading to widespread litigation and supply chain failures (Hogan Lovells).
Tip: Automating clause review with Leah, ContractPodAi’s AI assistant helps spot missing protections and benchmark against industry best practices.
What Legal & Compliance Risks Should Manufacturing Contracts Address?
Manufacturing contracts must account for:
- International trade – import/export controls, tariffs, trade agreement benefits (USMCA, CPTPP, EU)
- Industry-specific regulation – FDA (pharma), CE marking (EU), IATF 16949 (auto), HACCP (food)
- 2025 compliance trends – ESG metrics, carbon reporting, cyber resilience, AI governance, supplier diversity
- Labor & environmental laws – workplace safety, ethical sourcing, waste reduction
- Anti-corruption clauses – bribery prevention, conflict minerals, global ethics codes
Recent events underscore why strong compliance language is essential. Volatility in global shipping caused by new tariffs and geopolitical conflict has already disrupted supply chains and increased costs for manufacturers. Companies that fail to include comprehensive risk allocation and trade compliance provisions in their contracts may find themselves unable to respond effectively to these external shocks. Building flexibility into your agreements—through tariff pass-through mechanisms, logistics contingency clauses, or force majeure updates—can help mitigate these risks (Reuters).
How Should You Negotiate Manufacturing Contracts Effectively?
Navigating the legal landscape is critical to avoiding costly disputes and ensuring operational compliance. Manufacturing contracts must address multiple layers of legal requirements that vary by jurisdiction, industry, and product type.
International Manufacturing Considerations
Import/Export Regulations and Tariffs: Cross-border manufacturing requires compliance with customs regulations, trade agreements, and tariff classifications. Contracts should specify responsibility for customs clearance, duty payments, and compliance with export control laws.
Trade Agreement Benefits: Leverage benefits from agreements like USMCA, CPTPP, or EU trade deals by including origin certification requirements and documentation procedures.
Industry-Specific Regulatory Requirements
FDA Validation (Pharmaceuticals): Manufacturing contracts for pharmaceutical products must include Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) compliance, validation protocols, and FDA inspection readiness procedures.
CE Marking (Europe): Products sold in European markets require CE conformity marking, necessitating compliance with applicable EU directives and standards documentation.
Automotive Safety Standards: Manufacturing contracts in automotive industry must address ISO/TS 16949 compliance, safety recall procedures, and supply chain traceability requirements.
2025 Compliance Trends
ESG (Environmental, Social, Governance) Requirements: Modern manufacturing contracts increasingly include sustainability metrics, carbon footprint reporting, and ethical sourcing requirements. Companies are incorporating supplier diversity goals and environmental impact assessments.
Cybersecurity Clauses: With increasing digitalization, contracts must address data protection, cyber security standards, and incident response procedures. This includes compliance with GDPR, CCPA, and other data protection regulations.

AI Governance: As artificial intelligence becomes prevalent in manufacturing, contracts need provisions for AI system transparency, algorithmic accountability, and automated decision-making oversight.
Practical Legal Risk Mitigation
Labor Law Considerations: Ensure compliance with local labor laws, including working conditions, wage requirements, and worker safety standards. This is particularly important for international manufacturing relationships.
Environmental and Sustainability Requirements: Address environmental regulations, waste disposal requirements, and sustainability reporting obligations that are becoming increasingly stringent globally.
Anti-Corruption and Ethical Sourcing: Include anti-bribery clauses, conflict mineral compliance, and ethical sourcing requirements, particularly for international supply chains.
Key Mitigation Strategies:
- Conduct regular compliance audits and assessments
- Maintain updated regulatory change monitoring systems
- Include regulatory change adaptation clauses in contracts
- Establish clear documentation and record-keeping requirements
- Implement supplier qualification and ongoing monitoring programs
Manufacturing Contract Negotiation Best Practices
Effective negotiation is key to securing favorable terms while building sustainable partnerships. Here are proven strategies for successful manufacturing contract negotiations:
Pre-Negotiation Preparation
Due Diligence Checklist:
- Assess manufacturer’s financial stability and production capacity
- Review quality certifications and compliance history
- Evaluate technical capabilities and equipment condition
- Analyze past performance with similar projects
- Understand manufacturer’s customer base and industry experience
Capacity Assessment: Verify the manufacturer’s ability to meet your volume requirements, including surge capacity for seasonal demands or unexpected growth.
Key Negotiation Points
Pricing Strategy: Focus on total cost of ownership rather than just unit price. Consider tooling costs, setup fees, minimum order quantities, and volume-based pricing tiers.
Quality Assurance: Negotiate comprehensive quality control procedures, including incoming material inspection, in-process monitoring, and final product testing protocols.
Intellectual Property Protection: Establish clear ownership rights, licensing terms, and confidentiality protections. Include provisions for IP indemnification and unauthorized use penalties.
Termination Flexibility: Negotiate reasonable termination clauses that provide exit options without excessive penalties, including inventory buyback provisions and transition assistance.
Common Negotiation Mistakes to Avoid
Vague Specifications: Avoid general descriptions that can lead to disputes. Provide detailed technical specifications, quality standards, and performance requirements.
Inadequate IP Protection: Don’t underestimate the importance of comprehensive intellectual property clauses, especially for proprietary designs or processes.
Poor Payment Terms: Avoid payment structures that create cash flow problems for either party. Balance manufacturer financing needs with your risk tolerance.
Insufficient Insurance Requirements: Ensure adequate insurance coverage for product liability, errors and omissions, and general commercial risks.
Weak Dispute Resolution: Establish clear escalation procedures and efficient dispute resolution mechanisms to avoid costly litigation.
Leveraging Technology in Negotiations
AI Contract Analysis: Utilize AI-powered tools to analyze contract terms, identify potential risks, and benchmark against industry standards.
Automated Redlining: Use technology to streamline the redlining process and track negotiation history for future reference.
Real-Time Compliance Monitoring: Implement systems that monitor regulatory changes and automatically update contract terms as needed.
Pro Tip: Successful negotiations focus on creating win-win outcomes rather than extracting maximum concessions. Building strong relationships with manufacturers often leads to better pricing, priority treatment during capacity constraints, and collaborative problem-solving when issues arise.
How Is AI Changing the Way Manufacturing Contracts Are Managed?
AI is reshaping contract lifecycle management in 2025 by transforming how agreements are created, monitored, and optimized. Large language models (LLMs) trained on legal and industry data can now analyze thousands of clauses in minutes, identifying risks, inconsistencies, and compliance gaps with far greater accuracy than manual review. These systems also deliver automated clause recommendations, ensuring consistent language across contracts and embedding best practices at scale. Beyond analysis, predictive models forecast potential delivery delays, supplier risks, or quality problems before they occur, while real-time compliance monitoring tracks evolving regulations across multiple jurisdictions.
What’s driving this shift is the rise of agentic AI—systems that don’t just respond, but proactively manage workflows. Integrated into contract lifecycle platforms, agentic AI can initiate redlining, monitor supplier performance, and even trigger alerts or draft amendments when regulatory or commercial conditions change. Modern platforms often combine multiple LLMs, each tuned for different tasks—from clause interpretation, to compliance validation, to supply chain integration—so organizations get specialized intelligence rather than relying on a single model. As AI-powered robotics transform factory floors, AI in contracts ensures that these complex manufacturing partnerships are governed with the same level of precision and foresight.
For a deeper look at how this works in practice, see ContractPodAi’s approach to Agentic AI.
What Industry-Specific Requirements Should You Know?
Different industries have unique regulatory, technical, and operational requirements that must be reflected in manufacturing contracts. Understanding these industry-specific needs is crucial for creating effective agreements.
Electronics Manufacturing
Key Requirements:
- IP Protection: Comprehensive protection for proprietary designs, firmware, and technical specifications
- Component Sourcing: Traceability requirements for critical components and conflict mineral compliance
- Quality Standards: IPC standards compliance, testing protocols, and failure analysis procedures
- Technology Transfer: Secure handling of design files, manufacturing data, and technical documentation
- Regulatory Considerations: ROHS compliance, FCC certification requirements, and export control regulations for advanced technologies.
Pharmaceutical Manufacturing
Key Requirements:
- FDA Validation: Current Good Manufacturing Practice (cGMP) compliance and validation protocols
- Quality Systems: Comprehensive quality management systems with full traceability and documentation
- Regulatory Compliance: FDA inspection readiness, batch record management, and adverse event reporting
- Serialization: Track-and-trace requirements for prescription drugs and medical devices
- Unique Considerations: Technology transfer validation, clinical trial material handling, and stability testing requirements.
Food Manufacturing
Key Requirements:
- HACCP Compliance: Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points system implementation
- Food Safety Standards: FDA, USDA, or relevant international food safety certifications
- Labeling Requirements: Nutritional information, allergen declarations, and country-of-origin labeling
- Traceability Systems: Complete supply chain traceability for food safety incident response
- Regulatory Focus: Preventive Controls for Human Food regulation, supplier verification programs, and recall procedures
Automotive Manufacturing
Key Requirements:

- Safety Standards: IATF 16949 quality management system compliance and safety-critical component protocols
- Supply Chain Complexity: Multi-tier supplier management and just-in-time delivery requirements
- Recall Procedures: Comprehensive recall planning and traceability systems for safety defects
- Performance Standards: Warranty provisions, performance testing, and continuous improvement requirements
- Emerging Considerations: Electric vehicle component requirements, autonomous vehicle technology standards, and cybersecurity for connected vehicles
Textiles/Apparel Manufacturing
Key Requirements:
- Labor Compliance: Fair labor standards, workplace safety, and social responsibility requirements
- Sustainability Standards: Environmental impact requirements, sustainable material sourcing, and waste reduction goals
- Design Protection: Protection for fashion designs, patterns, and brand elements
- Quality Control: Fabric testing, sizing consistency, and durability standards
Global Considerations: Compliance with international labor standards, environmental regulations, and trade agreement requirements.
Each industry requires specialized contract language that addresses sector-specific risks, regulatory requirements, and operational challenges. Working with experienced legal counsel familiar with your industry is essential for developing comprehensive manufacturing agreements.
What Common Mistakes Do Businesses Make in Manufacturing Contracts?
Understanding common pitfalls can prevent costly disputes and operational disruptions. Here are the most frequent mistakes and their solutions:
Vague Quality Specifications
The Problem: General statements like “industry standard quality” or “acceptable quality” create ambiguity and disputes over what constitutes acceptable products.
Solution: Include detailed technical specifications, measurable quality metrics, testing procedures, and clear acceptance criteria. Define quality standards with specific tolerances and testing methodologies.
Inadequate IP Protection
The Problem: Failing to clearly define intellectual property ownership, licensing rights, and confidentiality protections, leading to IP theft or unauthorized use.
Solution: Comprehensive IP clauses that address existing IP, jointly developed IP, licensing terms, and protection mechanisms. Include IP indemnification and regular IP audits.
Preventative Measure: Implement secure data sharing protocols and regular IP compliance monitoring.
Poor Termination Clauses
The Problem: Termination clauses that are too restrictive or lack clear procedures for contract exit, creating costly obligations or lengthy disputes during contract termination.
Solution: Balanced termination provisions with reasonable notice periods, clear termination triggers, inventory buyback provisions, and transition assistance requirements.
Best Practice: Include both convenience termination and cause-based termination options with appropriate penalties and procedures.
Insufficient Insurance Requirements
The Problem: Inadequate insurance coverage that doesn’t protect against manufacturing-specific risks like product liability, professional indemnity, or business interruption.
Solution: Comprehensive insurance requirements including general liability, product liability, professional indemnity, and cyber liability coverage with appropriate limits and additional insured provisions.
Risk Mitigation: Regular insurance reviews and certificate monitoring to ensure continuous coverage.
Overlooking Regulatory Compliance
The Problem: Failing to address industry-specific regulations, changing compliance requirements, or international regulatory differences.
Solution: Include comprehensive compliance clauses, regulatory change procedures, and regular compliance audits. Address jurisdiction-specific requirements for international manufacturing.
Monitoring System: Implement regulatory change tracking and automatic contract update procedures.
Weak Dispute Resolution Mechanisms
The Problem: Litigation-focused dispute resolution that creates adversarial relationships and expensive legal proceedings.
Solution: Multi-tier dispute resolution including direct negotiation, mediation, and arbitration. Include escalation procedures and relationship preservation mechanisms.
Strategic Approach: Focus on maintaining business relationships while protecting legal rights.
Ignoring Force Majeure Considerations
The Problem: Outdated or inadequate force majeure clauses that don’t address modern risks like cyber attacks, pandemic disruptions, or supply chain failures.
Solution: Comprehensive force majeure provisions that include cyber incidents, public health emergencies, supply chain disruptions, and clear mitigation obligations.
Update for 2025: Include cyber incidents, pandemics, remote work requirements, and supply chain failures in force majeure clauses.
Poor Payment Term Structure
The Problem: Payment terms that create cash flow problems, lack clarity on payment triggers, or don’t address currency fluctuations in international contracts.
Solution: Balanced payment structures with clear milestones, reasonable payment terms, currency hedging provisions, and late payment penalties.
Financial Protection: Include credit protection mechanisms and regular financial health monitoring of manufacturing partners.
What you need to know about Templates & Resources?
Creating effective manufacturing contracts requires access to proper templates, resources, and expert guidance. Here’s a comprehensive guide to available resources and best practices for contract development:
Template Guidance and Structure
While specific templates vary by industry and contract type, effective manufacturing contracts should follow a structured approach:
Essential Template Components:
- Executive summary with key terms and parties
- Detailed scope of work and specifications
- Performance standards and quality requirements
- Payment terms and pricing mechanisms
- Intellectual property and confidentiality provisions
- Compliance and regulatory requirements
- Risk allocation and insurance provisions
- Termination and dispute resolution procedures
Customization Considerations: Templates must be adapted for specific industries, jurisdictions, and business relationships. Generic templates often miss critical industry-specific requirements or regulatory compliance needs.
ContractPodAi Resources
AI-Powered Contract Templates: ContractPodAi provides intelligent contract templates that automatically adjust based on your industry, contract type, and risk preferences. These templates incorporate best practices and regulatory requirements specific to your business needs.
Contract Analysis Tools: Advanced AI analysis capabilities review your existing contracts, identify gaps or risks, and suggest improvements based on industry benchmarks and legal best practices.
Automated Compliance Monitoring: Real-time monitoring of regulatory changes with automatic alerts when contract updates may be required to maintain compliance.
Industry Association Resources
Manufacturing-Specific Organizations: Industry associations often provide contract guidance, template resources, and best practice recommendations tailored to specific manufacturing sectors.
Trade Association Benefits: Membership in relevant trade associations provides access to legal resources, contract templates, and industry-specific compliance guidance.
Legal Review Recommendations
When to Engage Legal Counsel:
- High-value contracts or complex manufacturing relationships
- International manufacturing arrangements
- Highly regulated industries (pharmaceuticals, aerospace, automotive)
- Contracts involving significant IP or proprietary technology
- First-time manufacturing partnerships
Legal Review Process: Establish procedures for legal review that balance thoroughness with efficiency, including template pre-approval and standard clause libraries.
Legal Review Recommendations
When to Engage Legal Counsel:
- High-value contracts or complex manufacturing relationships
- International manufacturing arrangements
- Highly regulated industries (pharmaceuticals, aerospace, automotive)
- Contracts involving significant IP or proprietary technology
- First-time manufacturing partnerships
Legal Review Process: Establish procedures for legal review that balance thoroughness with efficiency, including template pre-approval and standard clause libraries.
What Should Be on Your Final Contract Review Checklist?
Pre-Execution Review:
- Verify all required approvals and signatures
- Confirm insurance certificates and compliance documentation
- Review payment terms and credit protections
- Validate technical specifications and quality requirements
- Ensure regulatory compliance documentation
Ongoing Management:
- Monitor performance against contract terms
- Track compliance with quality and delivery requirements
- Review and approve any contract modifications
- Maintain updated contact information and key personnel
- Prepare for contract renewal or termination decisions
What’s Changing in Manufacturing Contracts in 2025?
Manufacturing contracts in 2025 are evolving rapidly to reflect new business realities. Sustainability has become central, with ESG-focused clauses now embedded directly into agreements to address carbon accountability and ethical sourcing.
At the same time, AI-driven tools are being used to monitor compliance and assess supplier risks in real time, giving organizations far greater visibility into their global supply chains. Volatility in tariffs and raw material costs has also led to the adoption of dynamic pricing provisions, ensuring that contracts can adapt to market fluctuations without constant renegotiation.
Meanwhile, reshoring and nearshoring strategies are reshaping supply chain contracts to reduce dependency on distant manufacturing hubs and improve resilience. Recent events, such as the Grasberg mine accident tightening global copper supplies, underscore why material volatility clauses are no longer optional but essential. Collectively, these shifts signal a new era in which manufacturing contracts serve not only as legal safeguards but as agile business tools designed to manage risk, support sustainability, and strengthen supply chain stability.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What exactly is a manufacturing contract?
A manufacturing contract is a legally binding agreement between a business and a manufacturer that defines how goods will be produced. It covers product specifications, quality standards, pricing, delivery, intellectual property (IP) rights, compliance obligations, and more. Unlike purchase orders, these contracts serve as comprehensive rulebooks for how production happens and how risks are managed.
2. Why are manufacturing contracts more important in 2025?
Contracts are no longer just legal formalities—they are strategic tools for managing global risks. With increasing supply chain disruptions, tariff volatility, ESG reporting requirements, and cybersecurity concerns, manufacturers need contracts that provide clarity, flexibility, and resilience. AI-powered contract lifecycle management (CLM) is also reshaping how businesses create, monitor, and enforce agreements.
3. What are the most common types of manufacturing contracts?
There are 17 contract types businesses rely on today, including Contract Manufacturing Agreements, OEM and ODM agreements, Private Label and White Label agreements, Supply Chain agreements, and industry-specific contracts for pharmaceuticals, textiles, food, and automotive. Each type addresses different needs—from outsourcing production, to ensuring compliance in regulated sectors, to protecting brand exclusivity.
4. What key clauses should every manufacturing contract include?
At a minimum, contracts should address:
- Intellectual property rights
- Confidentiality/NDA protections
- Quality control and product specifications
- Payment terms and pricing
- Delivery and performance terms
- Termination and renewal procedures
- Force majeure and risk allocation
- Indemnification and liability caps
- Compliance and regulatory obligations
- Dispute resolution mechanisms
5. What are the biggest mistakes companies make in manufacturing contracts?
Common pitfalls include: vague product specifications, inadequate IP protection, restrictive termination clauses, insufficient insurance requirements, weak compliance coverage, outdated force majeure clauses, and poorly structured payment terms. Each of these issues has historically led to costly disputes, recalls, or business interruptions.
6. How is AI transforming manufacturing contract management?
AI tools—including multiple specialized large language models (LLMs) and emerging agentic AI systems—are now analyzing thousands of clauses in minutes, spotting risks, benchmarking against industry standards, and even drafting recommendations. Beyond review, AI can proactively redline contracts, trigger alerts for regulatory changes, and forecast supplier performance risks. This shift is making contracts more adaptive, consistent, and resilient.
7. What legal and compliance risks should manufacturers watch for?
Manufacturing contracts in 2025 must address:
- Trade compliance (import/export controls, tariffs, trade agreements)
- Industry-specific regulations (FDA, IATF 16949, HACCP, CE marking)
- Emerging requirements (ESG reporting, AI governance, cybersecurity clauses)
- Labor and environmental laws (ethical sourcing, worker safety, waste reduction)
- Anti-corruption rules (bribery, conflict minerals, transparency codes)
8. How should businesses approach contract negotiations?
Effective negotiation starts with due diligence—understanding a manufacturer’s capacity, compliance history, and financial stability. Companies should focus on total cost of ownership, detailed quality assurance processes, IP protections, balanced termination clauses, and robust insurance coverage. Using AI tools during negotiation helps flag risks, speed up redlining, and ensure compliance with evolving regulations.
9. Are templates useful for manufacturing contracts?
Yes—but only as a starting point. Generic templates often miss industry-specific requirements or jurisdictional nuances. Best practice is to use AI-powered smart templates, like those from ContractPodAi, that adjust to your industry, risk profile, and compliance obligations. Final drafts should always undergo legal review, especially for high-value or international manufacturing relationships.
10. What’s new in manufacturing contracts in 2025?
Key trends include:
- ESG and sustainability metrics written into contracts
- AI-driven monitoring of compliance and supplier risk
- Dynamic pricing clauses to handle tariff and raw material volatility
- Reshoring and nearshoring reflected in supply chain agreements
- Expanded force majeure definitions (cyber incidents, pandemics, logistics crises)
Well-crafted manufacturing contracts are no longer merely legal necessities—they’re strategic business tools. By combining robust contract drafting with AI-powered CLM solutions like ContractPodAi’s Leah, organizations can reduce risk, accelerate performance, and strengthen supplier relationships in 2025 and beyond.


