Published: July 2, 2024
Updated: May 21, 2025
The AI Revolution in Legal Practice
AI is transforming legal work. Master AI prompting to save time, increase accuracy, and improve client outcomes. For legal professionals, knowing how and when to use AI is now essential.

According to the latest data, adoption of AI in the legal profession has increased dramatically, with 79% of law firm respondents anticipating that AI will have a high or transformational impact on their work within the next five years, as reported by the Thomson Reuters Future of Professionals Report. However, despite this growing recognition, many legal professionals still lack confidence in their ability to craft effective prompts.
This guide draws on our extensive experience to provide you with actionable strategies for mastering AI prompts specifically tailored to legal applications in 2025 and beyond.
Understanding Different Types of AI Technologies in Legal Practice
Before diving into prompt engineering, it’s important to understand the various AI technologies transforming legal practice:
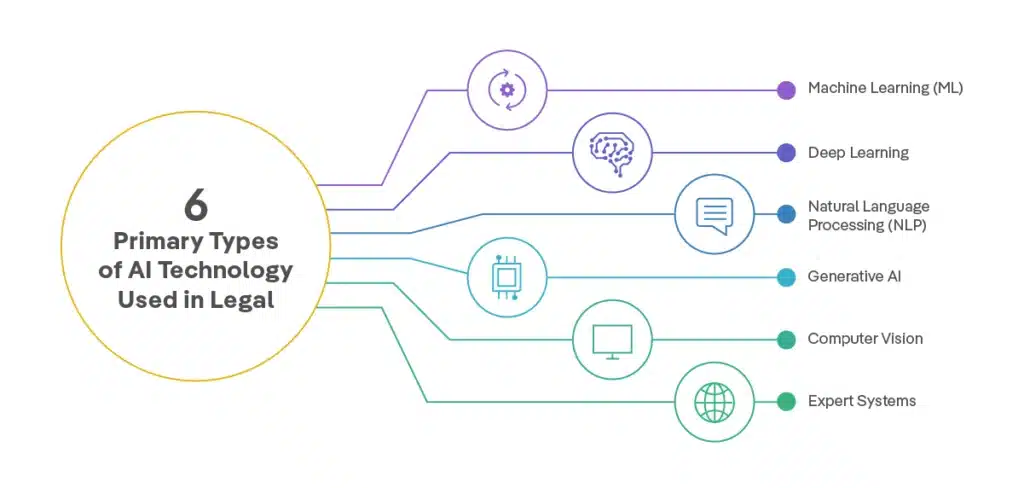
Machine Learning (ML)
Recommends case law citations based on semantic similarity, improving with experience rather than explicit programming.
Deep Learning
Utilizes deep neural networks with multiple layers to predict case outcomes and judicial decisions.
Natural Language Processing (NLP)
Enables machines to understand, interpret, and generate human language, useful for drafting legal documents and processing plain language queries.
Generative AI
Creates content like text or code based on training patterns. Legal teams use it to draft documents like NDAs with specific client requirements.
Computer Vision
Interprets visual information, assisting with document discovery and litigation support.
Expert Systems
Answers questions using rule-based systems, providing contract drafting advice and case management recommendations.
Understanding AI Prompt Engineering: The ABCDE Framework
Prompt engineering—the art and science of constructing inputs that yield optimal AI outputs—requires a structured approach, especially in the legal domain where precision is paramount.
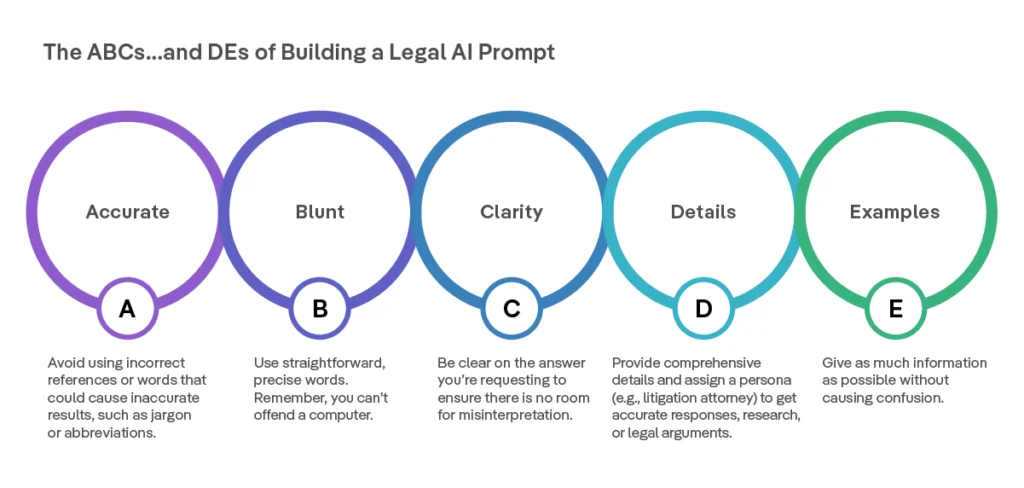
The ABCDE Framework for Legal Professionals
The ABCDE framework provides a systematic approach to crafting effective legal prompts:
- A – Audience/Agent Definition: Clearly define the AI’s role and expertise level
- B – Background Context: Provide relevant case details, legal standards, or jurisdictional information
- C – Clear Instructions: Specify exact deliverables and format requirements
- D – Detailed Parameters: Set scope, tone, length, and citation requirements
- E – Evaluation Criteria: Include standards for assessing the response quality
This structured approach transforms a vague request into a precise prompt, guiding the AI to produce a first draft ready for a professional to review and from which they can begin working.
Example: Transforming a Basic Prompt Using the ABCDE Framework
Basic Prompt: “Write a demand letter.”
Enhanced Prompt Using ABCDE:
- A – Agent: Act as an experienced commercial litigation attorney with expertise in breach of contract claims in California
- B – Background: My client, ABC Manufacturing, entered into a supply agreement with XYZ Corp on January 15, 2024. XYZ has failed to deliver the contracted materials for 45 days despite multiple notifications
- C – Clear Instructions: Draft a formal demand letter requesting immediate delivery of materials and compensation for business interruption
- D – Detailed Parameters: The letter should be professionally formatted, approximately 700 words, cite relevant California Commercial Code provisions, and include standard legal notices
- E – Evaluation Criteria: The letter should be assertive but not antagonistic, legally sound, and persuasive without making unsupportable claims

Advanced Prompt Techniques for Legal Applications
Prompt Chaining for Complex Legal Analysis
Complex legal tasks often require breaking down the analysis into sequential steps. Prompt chaining—using the output of one prompt as input for subsequent prompts—can significantly enhance results for tasks like due diligence or regulatory compliance analysis. Each prompt should also build logically on the previous statement, to enable the AI to perform linked tasks with greater understanding.
Example Prompt Chain for Contract Risk Assessment:
- Initial Analysis Prompt: “Identify all force majeure clauses in the attached agreement.”
- Follow-up Prompt: “Using the force majeure clauses you identified, analyze potential vulnerabilities under current California case law regarding pandemic-related business disruptions.”
- Final Prompt: “Based on your analysis, suggest three specific amendments to strengthen the force majeure provisions against identified vulnerabilities.”
Leveraging AI Prompt Generators for Legal Tasks
Creating effective prompts from scratch can be challenging, especially for legal professionals new to AI. Prompt generators specifically designed for legal applications can help bridge this gap by providing templates and frameworks tailored to common legal tasks.
These tools help legal professionals quickly generate effective prompts for various legal scenarios without needing to master prompt engineering principles themselves. By answering a few questions about the specific legal task, context, and desired output, attorneys can generate sophisticated prompts that yield higher-quality AI responses.
For example, our “AI Prompt Generator for Lawyers” custom GPT helps create customized prompts for common legal tasks like contract drafting, legal research, case analysis, and document review. This tool can be particularly valuable for legal teams looking to standardize their approach to AI across the organization and ensure consistent, high-quality outputs.
System vs. User Prompts: Strategic Framing
Many AI systems distinguish between “system” prompts (setting overall parameters) and “user” prompts (specific requests). Legal professionals can leverage this distinction for more effective results.
|
Types of Prompts |
Purpose |
Example |
|
System Prompt |
Sets the overall context and parameters |
“You are an expert legal researcher with deep knowledge of Delaware corporate law. You provide concise, well-structured analyses with proper legal citations using Bluebook format. You distinguish clearly between established law and areas of legal uncertainty.” |
|
User Prompt |
Makes specific requests within the context of the query |
Analyze the fiduciary duty implications of a board’s decision to reject an unsolicited acquisition offer that presented a 30% premium over current market value.” |
This two-tiered approach establishes a consistent analytical framework while allowing for specific inquiries within that framework.
The Legal Professional’s Prompt Clinic: Before and After Examples
Case Study 1: Legal Research Optimization
Before (Weak Prompt): “What are the requirements for patent infringement?”
After (Strong Prompt): “Provide a structured analysis of the elements required to establish direct patent infringement under 35 U.S.C. § 271(a) as interpreted by Federal Circuit decisions from 2022-2025. Include the standard of proof, distinguish between literal infringement and the doctrine of equivalents, and cite three recent leading cases that have refined the analysis.”
Annotation: The enhanced prompt specifies:
- The exact legal question (direct infringement under specific statute)
- Jurisdictional scope (Federal Circuit)
- Timeframe (2022-2025)
- Specific analytical components (standard of proof, infringement types)
- Output requirements (citations to three recent cases)
This prompt is superior because it specifies the statute, jurisdiction, timeframe, analytical components, and output requirements.
Case Study 2: Contract Drafting Enhancement
Before (Weak Prompt): “Draft a confidentiality agreement.”
After (Strong Prompt): “Draft a mutual non-disclosure agreement between a SaaS provider and an enterprise customer in the healthcare sector. The agreement should:
- Include standard definitions for confidential information with specific carve-outs for HIPAA-regulated data
- Provide for a 3-year confidentiality period following disclosure
- Include appropriate exceptions for information independently developed or publicly available
- Incorporate New York governing law and venue provisions
- Be approximately 5 pages in standard legal format
- Use plain language where possible while maintaining legal enforceability.”
Annotation: The enhanced prompt provides crucial context (parties, industry), specific content requirements, jurisdictional information, and format specifications.
Practical Applications: AI Prompts Across Legal Workflows
Document Review and Due Diligence
AI excels at processing large volumes of legal documents to identify specific provisions, inconsistencies, or risks.
Effective Prompt Example: “Review the attached 50-page commercial lease agreement and:
- Identify all provisions related to early termination rights for both landlord and tenant
- Extract key financial obligations, including base rent, CAM charges, and security deposit requirements
- Flag any unusual or non-standard provisions compared to typical Class A office leases in Los Angeles
- Create a table summarizing all identified provisions with clause numbers and page references
- Highlight potential risks or ambiguities in the termination provisions
Legal Research Enhancement
While AI cannot replace traditional legal research platforms, it can significantly accelerate preliminary research and analysis.
Effective Prompt Example: “I’m researching the evolving standards for establishing personal jurisdiction based on internet activities. Please:
- Summarize the key holdings from International Shoe through Ford Motor Co. v. Montana that establish the framework for minimum contacts analysis
- Identify the leading federal circuit cases from 2022-2025 that specifically address when online activities constitute ‘purposeful availment’ in the forum state
- Highlight any circuit splits on this issue
- Structure your response as an annotated timeline showing the evolution of these standards with brief explanations of each key development.”
Efficiency Gain: AI could save lawyers 4 hours per week while generating approximately $100,000 in new billable time per lawyer annually, according to Thomson Reuters’ 2024 Future of Professionals Report.
Contract Generation and Analysis
Contract drafting and review represent prime opportunities for AI-assisted efficiency gains.
Effective Prompt Example: “Using ContractPodAi’s template library, generate a first draft of a software development agreement with the following specifications:
- Client: ABC Healthcare (regulated entity under HIPAA)
- Developer: XYZ Software Solutions (independent contractor relationship)
- Project: Custom EMR integration module
- Key provisions to include:
- Robust IP assignment clauses for custom deliverables
- Source code escrow provisions
- HIPAA business associate agreement integration
- Milestone-based payment structure
- Acceptance testing procedures
- Limitation of liability capped at 2x contract value
- Governing law: California
For a deeper dive into real-world applications of AI in contract management and to explore specific use cases for in-house legal teams, download our comprehensive white paper: Real Use Cases for In-house Legal Teams. This resource provides practical examples of how legal departments are successfully implementing AI to transform their contract workflows and achieve measurable efficiency gains.
Spotlight on AI Tools: Leah
ContractPodAi’s Leah, designed exclusively for legal and compliance use cases, leverages agentic AI and best-of-breed Large Language Models (LLMs) to take the guesswork out of effective prompts. 
Leah, your own personalized Agentic AI solution, makes it effortlessly simple to perform legal responsibilities faster, smarter, and with total confidence. It incorporates ethical guardrails and rigorous testing, and her actions align with your organization’s standards, fostering trust in AI solutions.
Leah offers specialized legal modules that are rigorously tested for maximum accuracy:
- Extract: Pull key information from legal documents
- Contract Review: Compare and contrast contract versions
- Discovery: Find relevant information across documents
- Deals: Streamline transaction workflows
- Claims: Manage legal claims efficiently
- Playbook: Apply standardized approaches
- Helpdesk: Answer legal questions in real-time
- Draft: Create legal documents from scratch
Leah AI is tailored specifically for contract management and legal operations, producing results that significantly enhance your legal workflows:
- Analyze contracts and create records
- Identify key clauses and compare them to historical data
- Find favorable language from past legal documents
- Provide guidance based on successful past negotiations
- Suggest clauses, terms, and redlines aligned with company objectives
- Offer insight into all vendor and customer contract data
- Accelerate negotiations with real-time data powered by predictive analytics
Workflow Integration Guide: Where AI Prompting Fits in Legal Processes
Litigation Support Workflow
Case Intake → [AI: Draft Case Summary] → Initial Assessment → [AI: Relevant Case Law Research] → Strategy Development → [AI: Draft Initial Pleadings] → Attorney Review & Finalization → Filing
Key Integration Points:
- Case analysis summaries
- Preliminary legal research
- Document organization and timeline creation
- Deposition preparation
- Draft pleadings and motions
Transactional Law Workflow
Client Requirements → [AI: Initial Term Sheet Generation] → [AI: First Draft Creation] → Attorney Review → [AI: Revision Implementation] → Negotiation → [AI: Comparison Analysis] → Finalization
Key Integration Points:
- Template selection and customization
- Red flag identification in opposing counsel drafts
- Clause alternatives generation
- Change tracking and document comparison
- Closing checklist creation
Ethical Considerations and Limitations of AI in Legal
Ultimately, however, attorneys remain responsible for the ethical and competent use of AI in their practice. While AI presents tremendous opportunities for legal professionals, there are important ethical considerations to keep in mind:
Bias and Fairness
AI systems develop decision-making based on training data which can inadvertently contain biases. Legal professionals must be vigilant about reviewing AI outputs for potential discrimination or unfair results.
Accuracy
When AI-generated content is inaccurate, it’s referred to as “hallucinations.” Lawyers must meticulously review any content suggested or edited by AI to prevent false citations or misrepresentations in legal filings.
Privacy and Confidentiality
Client confidentiality remains paramount when using AI tools. Not all platforms provide the same level of data protection or confidentiality safeguards.
Best Practice: Use enterprise-grade, legally-focused AI tools with appropriate confidentiality safeguards. ContractPodAi’s solutions are specifically designed to meet legal industry standards for data security and confidentiality.
Accountability
The ethical obligation to provide competent representation remains squarely with the attorney, regardless of AI utilization. ABA Model Rule 1.1 on competence has been interpreted in many jurisdictions to include understanding the benefits and risks of relevant technology.
Best Practice: Implement a systematic review process for all AI-generated content, treating AI as a highly capable assistant rather than a replacement for legal judgment.
Looking Ahead: The Future of AI Prompting in Legal Practice
The evolution of AI capabilities continues at a remarkable pace. Legal professionals who develop strong prompting skills now will be better positioned to leverage these advancements as they emerge.
Emerging Trends to Watch
- Multimodal AI systems that can analyze both text and visual documents, enhancing abilities to review complex exhibits, property records, and evidentiary materials
- Enhanced reasoning capabilities that improve handling of complex logical arguments central to legal analysis
- Industry-specific fine-tuning creating AI systems with deeper understanding of specialized legal domains
- Collaborative prompting interfaces that allow legal teams to jointly develop and refine prompts for complex matters
- Agentic AI technologies that can autonomously execute complex tasks based on human instructions. Learn how ContractPodAi is leading the way with agentic AI for contract management
Building a Continuous Learning Approach
The most successful legal professionals will adopt a continuous improvement mindset toward their AI prompting skills.
Recommended Approach:
- Maintain a prompt library of successful examples
- Implement regular “prompt reviews” to assess effectiveness
- Stay current with AI capability developments
- Share effective prompting strategies within your organization
- Regularly test new prompting techniques against established methods
Conclusion: The Competitive Advantage of Prompt Mastery
Prompt mastery is a key differentiator that allows legal professionals to fully harness AI’s potential—enhancing, not replacing, legal expertise. And as AI adoption accelerates, the ability to effectively communicate with AI tools (and other humans) will be a growing differentiator for successful practitioners.
The ABCDE framework, advanced techniques, and practical applications outlined in this guide provide a foundation for developing this crucial skill set. By systematically improving your prompting approach, you can harness AI as a powerful tool that enhances rather than replaces your legal expertise.
Taking the Next Step
To learn more about our Legal Agentic AI solution, Leah, get in touch with us today to schedule a demo.


