Published: November 12, 2019
Updated: Setpember 30, 2025
What is Contract Management?
Contract management involves creating, executing, and monitoring contracts to ensure compliance, mitigate risk, and achieve business goals. Key steps include drafting terms, negotiating agreements, tracking obligations, and managing renewals. Effective contract management reduces legal disputes and improves operational efficiency.

Why Contract Management Matters
Every day, businesses lose millions of dollars because someone, somewhere, missed a contract renewal date, overlooked a critical clause, or couldn’t find the right document when they needed it. If you’ve ever scrambled to locate a signed agreement before a crucial meeting or wondered why your organization keeps paying for services you no longer use, you already understand why contract management matters.
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of contract management fundamentals, from understanding the contract lifecycle to implementing effective systems that protect your business interests. Whether you’re managing contracts manually or exploring digital solutions, you’ll learn practical strategies to minimize risk, maximize revenue, and maintain compliance across your organization.
As someone who’s worked with organizations ranging from startups to Fortune 500 companies, I’ve seen firsthand how proper contract management transforms business operations. This guide draws on those experiences plus insights from legal professionals, procurement experts, and business leaders who’ve successfully implemented contract management systems.
Key Stages of Contract Management
- Contract request
- Drafting
- Negotiation
- Approval
- Execution
- Storage & tracking
- Renewal or termination
The Contract Lifecycle Explained
The contract lifecycle spans from initial request to final expiration or renewal. Understanding each phase helps you identify bottlenecks and opportunities for improvement.
Think of contract management like maintaining a car. Just as you don’t simply buy a vehicle and forget about it, contracts require ongoing attention through their entire lifecycle to perform optimally. The journey begins with request and initiation, where stakeholders identify the need for a new contract, gather initial requirements, and establish budgets and timelines.
During the authoring and drafting phase, legal teams create the initial contract draft, applying standard templates where possible while customizing terms for specific needs. This flows into negotiation and collaboration, involving multiple rounds of revisions between parties, internal stakeholder input collection, and finalization of key terms.
The review and approval stage ensures legal compliance, financial alignment, and executive buy-in. Once all parties agree, the execution phase involves preparing the final document, identifying appropriate signatories, and collecting signatures, whether electronic or traditional.
Post-execution, contracts enter the storage and repository management phase. Here, executed contracts are stored centrally with comprehensive metadata captured for easy retrieval and appropriate access permissions established. The compliance and performance monitoring phase tracks key dates, monitors obligations, and reviews performance metrics throughout the contract term.
Finally, contracts reach renewal or termination, where organizations assess renewal opportunities, follow termination procedures, and either begin a new cycle or end the relationship. Modern CLM (Contract Lifecycle Management) tools automate many of these processes, but understanding the fundamentals remains essential whether you’re working with paper files or sophisticated software.

Strategic Importance of Good Management
Contract management impacts every corner of your business. According to research by World Commerce and Contracting (formerly IACCM), poor contract management costs companies an average of 9.2% of annual revenue. This revenue leakage stems from missed renewal opportunities, overpayments on terminated contracts, penalties from non-compliance, and inability to enforce favorable terms.
While specific company examples are often proprietary, organizations across industries face significant fines when they can’t produce required documentation during audits. These contracts exist — they just can’t find them quickly enough. Proper contract management provides clear audit trails, regulatory compliance documentation, dispute resolution support, and liability protection.
When sales teams can access approved contract templates instantly rather than waiting days for legal review, deal cycles accelerate dramatically. Research indicates that organizations using contract management software report an 80% faster average cycle time from bid to signed agreement. This operational efficiency translates to faster time-to-revenue, reduced administrative burden, improved cross-departmental collaboration, and better resource allocation.
Organizations with mature contract management practices experience significant improvements in efficiency. Research shows that effective contract digitization boosts compliance by 55%, while contract management software can reduce administrative costs by 25-30%. This strategic advantage manifests as stronger vendor relationships, competitive pricing advantages, better negotiation positions, and enhanced market agility.

Common Challenges in Contract Management
Understanding typical obstacles helps you anticipate and avoid them. Most organizations store contracts across multiple systems — some in email, others in shared drives, physical filing cabinets, or departmental databases. This fragmentation creates duplicate contracts with conflicting terms, inability to locate critical documents, version control nightmares, and incomplete contract visibility. According to research from industry sources, 71% of companies cannot find 10% or more of their contracts.
Traditional contract workflows involve sequential handoffs between departments. Without automated alerts, organizations routinely miss auto-renewal deadlines, price increase notifications, compliance certification requirements, and termination windows.
When every department creates their own templates and processes, legal exposure increases through unapproved language, training becomes impossible, metrics remain inconsistent, and best practices never develop. Leadership teams need contract intelligence for strategic decisions, but manual systems rarely provide real-time obligation tracking, comprehensive risk assessments, spend analysis by vendor, or performance metrics.
Low-Tech vs. Comprehensive CLM Solutions
The evolution from basic digital tools to sophisticated CLM platforms represents more than feature enhancement — it’s a fundamental shift in how organizations approach contract lifecycle management. Low-tech solutions like shared drives and basic document management offer familiarity, lower initial costs, and minimal training requirements. You maintain simple workflows and can implement quickly with existing tools. However, the limitations quickly become apparent: fragmented processes across multiple systems, manual tracking and reporting, limited automation capabilities, basic search functionality, inconsistent approval workflows, and poor contract performance visibility.
Comprehensive CLM solutions transform these constraints into competitive advantages through end-to-end workflow automation, intelligent contract analytics, AI-powered clause extraction, integrated approval processes, automated compliance monitoring, advanced reporting dashboards, contract performance tracking, and seamless third-party integrations.
Choosing a CLM System
Selecting the right Contract Lifecycle Management system requires careful evaluation of your organization’s specific needs. Core features to evaluate include repository and search capabilities with OCR for scanned documents, advanced metadata tagging, full-text search, and bulk upload functionality. Workflow automation should offer customizable approval routing, parallel and sequential workflows, role-based permissions, and email notifications.
Reporting and analytics capabilities should include customizable dashboards, obligation tracking, spend analysis, and performance metrics. Integration capabilities must connect with your existing technology stack, including CRM systems like Salesforce or Microsoft Dynamics, ERP platforms like SAP or Oracle, e-signature tools like DocuSign or Adobe Sign, and communication platforms like Slack or Teams.
Create a vendor evaluation matrix considering total cost of ownership, implementation timeline, training requirements, customer support quality, security certifications, scalability options, and industry expertise. Leading CLM vendors include ContractPodAi, Ironclad, Icertis, and Agiloft, each offering unique strengths. ContractPodAi offers comprehensive AI embedded into every stage of the CLM platform plus agentic AI contract analytics. Ironclad focuses on workflow automation, Icertis provides enterprise scalability, and Agiloft offers customization options.
Implementation Roadmap
Before implementation, we recommend checking out ContractPodAi’s Maturity Model. Our maturity framework provides organizations with a clear roadmap for advancing their contract management capabilities through five distinct progression levels, each supported by six core operational pillars. This structured approach enables you to systematically evaluate your current state across critical areas including functional processes, governance structures, policy frameworks, procedural guidelines, and service delivery mechanisms.
Understanding your maturity level helps determine the scope and complexity of your implementation journey, ensuring you build the right foundation for long-term success.
Successful CLM implementation requires a structured approach that transforms good intentions into measurable business outcomes. The difference between transformative success and expensive failure often lies in following proven implementation methodologies. Our five-phase framework ensures systematic progress while maintaining organizational alignment and user adoption.
1. Kickoff
- Align stakeholders on vision and objectives
- Establish governance and ways of working together
- Formally kick off the project
2. Design
- Requirements validation workshops
- Map end-to-end business processes
- Integration design
- Document configuration requirements
- Sign-off on the Solution Design
3. Configure
- Configure platform per approved design
- Migrate legacy contracts
- Setup integrations
- Perform testing
- Develop training materials
4. Deploy
- User acceptance testing
- End-user training
- Production deployment
- Go-live readiness
5. Hypercare
- Monitor usage and adoption
- Provide post-go-live support
- Transition to continuous improvement
- Plan next phases
To ensure long-term success, the implementation can be seen as a new beginning for the future of the enterprise. Once your CLM system is in place, the real transformation begins—unlocking new efficiencies, enhancing compliance, and positioning your organization for future advancements. As we look ahead, the evolution of contract management is accelerating, and organizations that embrace innovation will gain a distinct competitive edge.
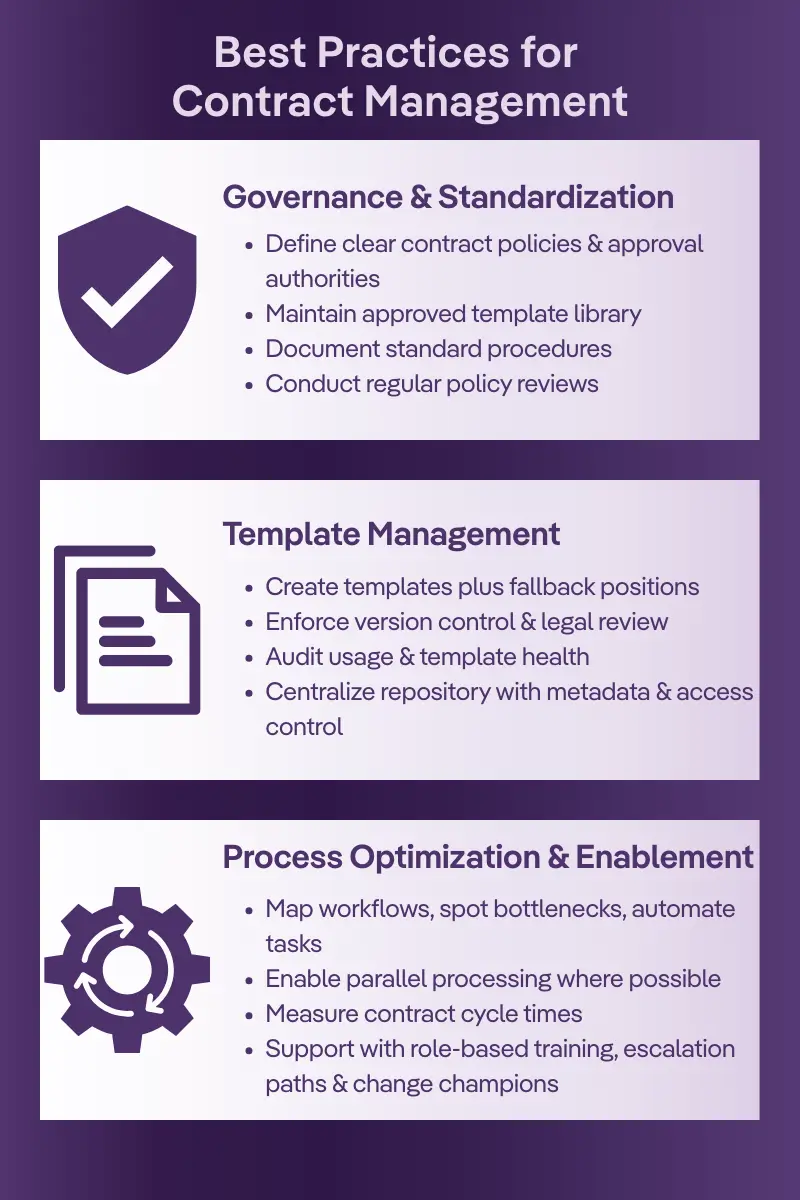
Best Practices for Contract Management
Whether using manual or digital systems, certain practices consistently improve outcomes. Establish clear contract policies, create an approved template library, define approval authorities, document standard procedures, and conduct regular policy reviews. This governance and standardization foundation enables consistent, compliant contract creation across your organization.
Template management requires developing templates for common scenarios, including approved fallback positions, maintaining version control, conducting regular legal reviews, and tracking template usage. Your centralized repository should serve as the single source of truth for all contracts, using consistent naming conventions, comprehensive metadata capture, regular repository audits, and proper access control management.
Process optimization involves mapping current workflows, identifying bottlenecks, implementing parallel processing where possible, automating repetitive tasks, and measuring cycle times. Support these technical improvements with role-specific training programs, regular refresher sessions, clear escalation paths, a change champion network, and a continuous improvement culture.
KPIs and Metrics
Measuring contract management performance drives continuous improvement across multiple dimensions. Efficiency metrics include contract cycle time from request to execution, average review time per stage, number of contracts processed monthly, percentage of contracts using templates, and first-time approval rates.
Compliance metrics track contracts with complete metadata, percentage with tracked obligations, audit readiness scores, regulatory compliance rates, and policy adherence percentages. Financial metrics encompass contract value under management, cost per contract processed, revenue at risk from expirations, savings from improved terms, and penalty avoidance value.
Risk metrics identify contracts without key dates tracked, high-risk clause frequency, vendor concentration analysis, contracts approaching expiration, and non-standard term usage. User adoption metrics monitor system login frequency, feature utilization rates, user satisfaction scores, support ticket volume, and training completion rates.
Compliance and Risk Management
Contract compliance extends beyond simple document storage. Different industries face unique regulatory requirements: healthcare organizations must ensure HIPAA compliance for patient data, financial institutions navigate SOX requirements for financial controls, technology companies address GDPR for data privacy, and government contractors follow FAR/DFARS regulations.
Internal compliance encompasses procurement policies, spending authorities, conflict of interest rules, document retention requirements, and security protocols. Implement a risk assessment framework that identifies contract risks across financial, operational, and legal dimensions, assesses probability and impact, develops mitigation strategies, monitors risk indicators, and reports to leadership.
Maintain comprehensive audit trails by documenting all contract changes, tracking access history, maintaining approval records, storing communication logs, and preserving version history.
Contract Review and Auditing
Regular contract audits ensure ongoing compliance and optimization. Implement spot check methodology through random sampling of active contracts, focusing on high-value agreements, reviewing compliance with policies, verifying data accuracy, and assessing process adherence.
Automated monitoring provides obligation tracking alerts, expiration notifications, performance metric monitoring, budget variance reporting, and compliance deadline tracking. Annual contract audits should include comprehensive repository reviews, process effectiveness assessments, technology utilization analysis, training needs identification, and policy update recommendations.
Integration with Other Systems
Modern CLM systems don’t operate in isolation. CRM integration with platforms like Salesforce or Microsoft Dynamics enables seamless quote-to-contract workflows, customer data synchronization, opportunity tracking, and revenue forecasting alignment. ERP connections to SAP or Oracle provide financial data integration, purchase order matching, budget validation, and spend analysis.
E-signature tool integration with DocuSign or Adobe Sign offers direct signature routing, status tracking, completed document storage, and audit trail preservation. Collaboration platform connections to Microsoft Suite, Google Suite, or Slack deliver real-time notifications, approval requests, status updates, and team communication.
Future of Contract Management
Emerging technologies continue to reshape contract management. Artificial intelligence enables automated contract analysis, risk identification, clause extraction, obligation discovery, and predictive insights. Studies show that AI outperformed trained lawyers by 10% in accuracy and can complete a contract review in just 26 seconds compared to 92 minutes for humans.
Natural language processing provides plain language contract summaries, multi-language support, sentiment analysis, automated redlining, and intelligent search capabilities. Blockchain technology promises smart contract execution, immutable audit trails, decentralized validation, automated payments, and trust verification. Predictive analytics delivers renewal likelihood scoring, negotiation outcome prediction, risk forecasting, performance trending, and spend optimization.
Final Thoughts: Getting Started
Your contract management journey depends on organizational maturity and specific needs.
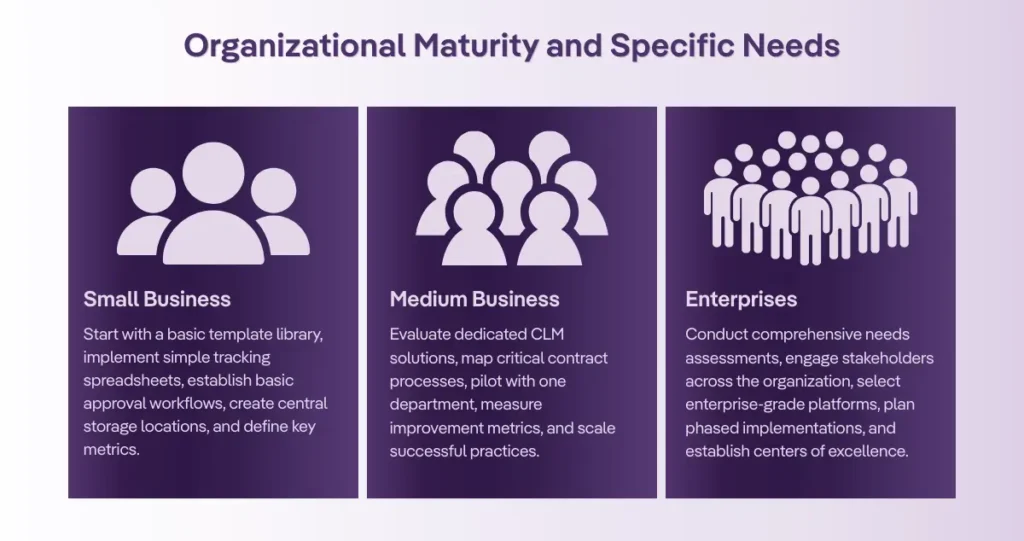
Small businesses should start with a basic template library, implement simple tracking spreadsheets, establish basic approval workflows, create central storage locations, and define key metrics.
Mid-size companies need to evaluate dedicated CLM solutions, map critical contract processes, pilot with one department, measure improvement metrics, and scale successful practices.
Enterprises must conduct comprehensive needs assessments, engage stakeholders across the organization, select enterprise-grade platforms, plan phased implementations, and establish centers of excellence.
Remember: perfect is the enemy of good. Start where you are, use what you have, and improve incrementally. Every step toward better contract management reduces risk and increases value.
Contract management fundamentally shapes how organizations operate, compete, and grow. While technology accelerates these processes, success ultimately depends on understanding core principles, implementing sound practices, and maintaining continuous improvement. Whether you’re managing ten contracts or ten thousand, the principles remain consistent: know what you have, track what matters, and optimize continuously. Your future self — and your organization — will thank you for starting this journey today.
Looking to improve your contract management process? Explore our CLM software comparison guide or talk to a legal tech expert.


